| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14194-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Backup and Recovery Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14194-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
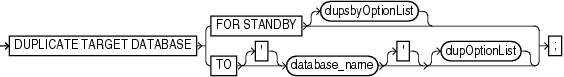
duplicate::=
logSpec::=
sizeSpec::=
To use backups (backup sets or image copies) of the target database to create either of the following:
A duplicate database, which is a copy of the target database (or a subset of the target database) with a unique DBID. Because a duplicate database has a unique DBID, it is entirely independent of the primary database and can be registered in the same recovery catalog as the primary database. Typically, duplicate databases are used for testing.
A standby database, which is a special copy of the primary database that is updated by applying archived redo logs from the primary database. A standby database does not get a new DBID.
To create a standby database with the DUPLICATE command you must specify the FOR STANDBY option. The DUPLICATE ... FOR STANDBY command creates the standby database by restoring a standby control file, mounting the standby control file, and then restoring and recovering backups of the target datafiles. The standby database is left mounted after duplication is complete. Note that backups of the standby database are interchangeable with backups of the primary database.
When duplicating a database that is currently in NOARCHIVELOG mode, recovery occurs with the NOREDO option. Hence, if incremental backups exist, RMAN applies only these backups to the restored files during recovery. For databases in ARCHIVELOG mode, DUPLICATE recovers by default up to the last archived redo log generated at the time the command was executed, or until a time specified with a SET UNTIL clause.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery Advanced User's Guide to learn how to create a duplicate database with the DUPLICATE command
Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration to learn how to create, manage, and back up a standby database
These restrictions apply to all uses of the DUPLICATE command (both for creation of a standby database and creation of a nonstandby duplicate database):
The target SCN for a DUPLICATE command cannot be before the most recent OPENRESETLOGS. DUPLICATE to previous incarnations is not supported.
Issue one or more ALLOCATE AUXILIARY CHANNEL commands before executing the DUPLICATE command, or CONFIGURE automatic auxiliary channels. RMAN uses the channel configuration from the target for auxiliary channels in the following circumstances:
You have not manually allocated auxiliary channels.
You have not configured auxiliary channels.
The automatic target channels do not have CONNECT strings.
The DUPLICATE command does not require non-AUXILIARY channels (that is, normal target database channels).
You must be connected to both the target database and auxiliary instance. The auxiliary instance must be started with the NOMOUNT option, and the target database must be mounted or open. The target database cannot be a standby database.
If you need to duplicate a database when some backups of the target database do not exist then you must specify SKIP TABLESPACE. If you do not specify SKIP TABLESPACE, then RMAN attempts to duplicate the following:
All datafiles in online tablespaces, whether or not the datafiles are online.
All tablespaces taken offline with an option other than NORMAL. For example, RMAN attempts to duplicate tablespaces taken offline with the IMMEDIATE option. You cannot duplicate OFFLINE NORMAL tablespaces, although you can add these tablespaces manually after duplication.
If no valid backups exist of any tablespace or datafile, then the DUPLICATE command fails.
You can skip all tablespaces in the target database except the SYSTEM tablespace, undo tablespaces, and tablespaces containing rollback segments. RMAN does not check for completeness. For example, you can duplicate a data tablespace but not the tablespace containing the index for the data, or duplicate a tablespace that contains only one partition of a partitioned table.
If the target and duplicate databases reside on the same host, set the CONTROL_FILES parameter appropriately so that the DUPLICATE command does not generate an error because the target control file is in use.
If the target and duplicate databases share the same host, set all *_PATH and *_DEST initialization parameters appropriately so that the target database files are not overwritten by the duplicate database files.
You cannot set the DB_NAME parameter in the duplicate parameter file to a value different from the database name specified in the DUPLICATE command.
You cannot use the same database name for the target and duplicate databases when the duplicate database resides in the same Oracle home as the target. Note that if the duplicate database resides in a different Oracle home from the target, then its database name just has to differ from other database names in that same Oracle home.
If the target and duplicate databases reside on different hosts, then you must do one of the following tasks for duplication to be successful:
Move backups and disk copies from the target host to the duplicate host to the same location as the target host so that the path names are identical
Move backups and disk copies from the target host to the duplicate host to a new location (so that the path names are different), and then CATALOG them.
Make sure that all backups and copies (disk or sbt) on the target host are remotely accessible from the duplicate host. Make sure that the archived redo logs are available in the expected location in the new host.
Duplication must be done to the same platform as the source datababse.
You cannot recover the duplicate database to the current point in time, that is, the most recent SCN. RMAN recovers the duplicate database up to or before the most recent available archived log: it cannot recover into the online redo logs.
Specify new filenames or convert target filenames for the datafiles and online redo logs when the duplicate filenames must be different from the target filenames (as when duplicating to the same host as the primary). If you do not specify filenames for duplicate online redo logs and datafiles, then RMAN reuses the target datafile names.
If you want the duplicate filenames to be the same as the target filenames, and if the databases are in different hosts, then you must specify NOFILENAMECHECK.
If duplicating a database on the same host as the target database, do not specify the NOFILENAMECHECK option. Otherwise, RMAN may signal this error:
RMAN-10035: exception raised in RPC: ORA-19504: failed to create file
"/oracle/dbs/tbs_01.f"
ORA-27086: skgfglk: unable to lock file - already in use
SVR4 Error: 11: Resource temporarily unavailable
Additional information: 8
RMAN-10031: ORA-19624 occurred during call to
DBMS_BACKUP_RESTORE.RESTOREBACKUPPIECE
The following restrictions and notes apply when you use the DUPLICATE command with the FOR STANDBY option:
All backups and copies located on disk must be available at the standby host with the same path names as in the target host.
Backups on tape must be accessible from the standby host.
If archived logs have not been backed up, then archived logs must be available at the standby host with the same path names as in the target host.
If RMAN recovers the standby database, then the checkpoint SCN of the control file must be included in an archived redo log that is either available at the standby site or included in an RMAN backup. For example, assume that you create the standby control file and then immediately afterward archive the current log, which has a sequence of 100. In this case, you must recover the standby database up to at least log sequence 100, or the database signals an ORA-1152 error message because the standby control file backup or copy was taken after the point in time.
You cannot use SET NEWNAME or CONFIGURE AUXNAME to transform the filenames for the online redo logs on the standby database.
You cannot use the DUPLICATE command to activate a standby database.
You cannot connect to the standby database and then DUPLICATE ... FOR STANDBY to create an additional standby database. To create additional standby databases, connect to the original primary database and run DUPLICATE ... FOR STANDBY.
Do not attempt to register the standby database in the primary database repository.
The DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT and LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT initialization parameters cannot be used to control generation of new names for files at the duplicate which are Oracle Managed Files (OMF) at the target database. When using Oracle Managed Files at the target instance, it is not generally possible to generate valid OMF filenames for the duplicate instance by replacing a substring of the target instance OMF filename. When duplicating Oracle Managed Files and storing the duplicates in an ASM disk group, RMAN uses DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT or LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT to convert the disk group name, and then generates a new, valid filename based on the converted disk group name.
You can avoid this issue by using one of the other supported options for naming datafiles being duplicated from OMF:
Use SET NEWNAME to specify names for individual datafiles
Use DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST for any datafile names not specifically renamed by SET NEWNAME, and do not specify DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT.
The supported options for naming online logs being duplicated from OMF are to use DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST, DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST or DB_CREATE_ONLINE_LOG_DEST_n. Do not use the LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameter.
When creating a standby or duplicate database and using Oracle Managed Files, tempfiles are re-created in the current DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST, either when the database is opened to become a primary, or when it is opened read-only. When not using Oracle Managed Files, DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT is used to convert the tempfile names for the new database. When the standby or duplicate database is opened in read-only or read/write mode, Oracle automatically creates temporary files as needed, with the converted names based upon DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT. To specify different filenames for the tempfiles, see the discussion of SWITCH TEMPFILE .
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
FOR STANDBY |
Specifies that database being duplicated is to be used as a standby database. RMAN restores the most recent files, unless SET UNTIL is specified. If DORECOVER is specified, then RMAN also recovers database. RMAN always leaves standby database in mounted state after executing DUPLICATE command. |
dupsbyOptionList |
Specifies options that only apply when creating a standby database. |
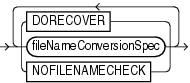
DORECOVER |
Specifies that RMAN should recover the database after creating it. If you specify an untilClause, then RMAN recovers to the specified point and leaves the database mounted. |
NOFILENAMECHECK |
Prevents RMAN from checking whether target datafiles sharing the same names as the duplicated files are in use. Note that the NOFILENAMECHECK option is required when the standby and primary datafiles and logs have identical filenames.
See Also: The description in |
TO 'database_name' |
Specifies the name of the duplicate database. The name should match the name in the initialization parameter file of the duplicate database or the database signals an error when creating the control file. |
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
dupOptionList |
Specifies options that apply when creating a duplicate database not intended for use as a standby database. |
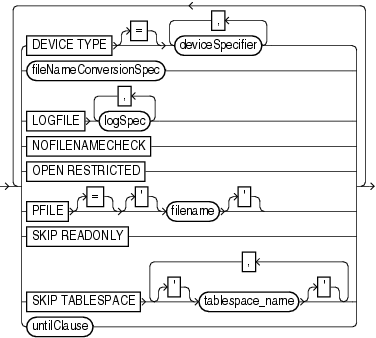
DEVICE TYPE deviceSpecifier |
Allocates automatic channels for the specific deviceSpecifier only (for example, DISK or sbt). This option is valid only if you have configured automatic channels and have not manually allocated channels. For example, if you CONFIGURE automatic disk and tape channels, and if you run DUPLICATE...DEVICE TYPE DISK, then RMAN allocates only disk channels.
See Also: "deviceSpecifier" |
| fileNameConversionSpec | Specifies one or more patterns to map original to duplicate filenames.
Note that this parameter overrides the initialization parameter See Also: "fileNameConversionSpec" |
LOGFILE logSpec |
Specifies the online redo logs when creating a nonstandby duplicate database. The syntax is the same used in the LOGFILE option of the CREATE DATABASE statement.
Refer to the description of |
NOFILENAMECHECK |
Prevents RMAN from checking whether target datafiles sharing the same names as the duplicated files are in use. The user is responsible for determining that the duplicate operation will not overwrite useful data.
This option is necessary when you are creating a duplicate database in a different host that has the same disk configuration, directory structure, and filenames as the host of the target database. For example, assume that you have a small database located in the /oracle/dbs/system_prod1.dbf /oracle/dbs/users_prod1.dbf /oracle/dbs/tools_prod1.dbf /oracle/dbs/rbs_prod1.dbf Assume that you want to duplicate the database in machine |
OPEN RESTRICTED |
Enables a restricted session in the duplicate database by issuing the following SQL statement: ALTER SYSTEM ENABLE RESTRICTED SESSION. RMAN issues this statement immediately before the duplicate database is opened. |
PFILE = 'filename' |
Specifies a client-side initialization parameter used by the auxiliary instance. RMAN automatically shuts down and restarts the auxiliary instance during duplication. If the auxiliary does not use a server-side parameter file in the default location, you must specify the client-side parameter file that RMAN should use when starting the auxiliary instance. Otherwise, you do not need to specify PFILE. |
SKIP READONLY |
Excludes datafiles in read-only tablespaces from the duplicate database.
Note: A record for the skipped read-only tablespace still appears in |
SKIP TABLESPACE 'tablespace_name' |
Excludes the specified tablespace from the duplicate database. Note that you cannot exclude the SYSTEM tablespace, undo tablespaces, and tablespaces with rollback segments. |
| untilClause | Sets the end point for incomplete recovery of the duplicate database. You can achieve the same result by running SET UNTIL before the DUPLICATE command.
See Also: "untilClause" |
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
logSpec |
Specifies the online redo logs when creating a nonstandby duplicate database. If you do not specify LOGFILE, then RMAN uses LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT if it is set. If neither LOGFILE nor LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT is set, then RMAN uses the original target log filenames for the duplicate files. You must specify the NOFILENAMECHECK option in this case.
See Also: Oracle Database SQL Reference for |
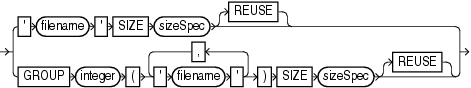
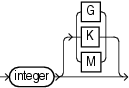
'filename' SIZE integer |
Specifies the filename of the online redo log member and the size of the file in kilobytes (K) or megabytes (M). The default is in bytes. |
REUSE |
Allows the database to reuse an existing file. If the file already exists, then the database verifies that its size matches the value of the SIZE parameter. If the file does not exist, then it is created. |
GROUP integer |
Specifies the group containing the online redo log members. |
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
dupsbyOptionList |
Specifies options that only apply when creating a standby database. |
DORECOVER |
Specifies that RMAN should recover the database after creating it. If you specify an untilClause, then RMAN recovers to the specified point and leaves the database mounted. |
| fileNameConversionSpec | Specifies how to convert original datafile names to new datafile names in the standby database.
See Also:"fileNameConversionSpec" |
NOFILENAMECHECK |
Prevents RMAN from checking whether target datafiles sharing the same names as the duplicated files are in use. Note that the NOFILENAMECHECK option is required when the standby and primary datafiles and logs have identical filenames.
See Also: The description in dupOptionList |
Setting New Filenames Manually: Example This example assumes that the target datafiles are on host1 in directory /h1/oracle/dbs/trgt. You wish to duplicate the database to newdb on host2 in the directory /h2/oracle/oradata/newdb. The DUPLICATE command uses backup sets stored on tape to duplicate the target database to database newdb, and recovers it to a point 24 hours ago:
RUN
{
ALLOCATE AUXILIARY CHANNEL newdb1 DEVICE TYPE sbt;
DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE TO newdb
DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT=('/h1/oracle/dbs/trgt/','/h2/oracle/oradata/newdb/')
UNTIL TIME 'SYSDATE-1' # specifies incomplete recovery
SKIP TABLESPACE cmwlite, drsys, example # skip desired tablespaces
PFILE = ?/dbs/initNEWDB.ora
lOGFILE
GROUP 1 ('?/oradata/newdb/redo01_1.f',
'?/oradata/newdb/redo01_2.f') SIZE 200K,
GROUP 2 ('?/oradata/newdb/redo02_1.f',
'?/oradata/newdb/redo02_2.f') SIZE 200K
GROUP 3 ('?/oradata/newdb/redo03_1.f',
'?/oradata/newdb/redo03_2.f') SIZE 200K REUSE;
}
Reusing the Target Filenames: Example This example assumes the following:
You are restoring to a new host without a catalog.
You have configured automatic channels.
The target host and duplicate host have the same file structure.
You wish to name the duplicate files exactly like the target database files.
You do not want to duplicate read-only tablespaces.
You want to prevent RMAN from checking whether files on the target database that have the same names as the duplicated files are in use.
CONNECT TARGET
CONNECT AUXILIARY SYS/aux_pwd@newdb
DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE TO ndbnewh
LOGFILE
'?/dbs/log_1.f' SIZE 200K,
'?/dbs/log_2.f' SIZE 200K
SKIP READONLY
NOFILENAMECHECK;
Creating a Standby Database: Example This example creates a standby database on a remote host with the same directory structure as the primary host. In this example, the NOFILENAMECHECK option is specified because the standby and primary datafiles and logs have the same names. Note that an automatic auxiliary channel is already configured, so you do not need to manually allocate a channel:
DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE FOR STANDBY NOFILENAMECHECK;