| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5) Part Number B31949-10 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 5 (10.2.0.5) Part Number B31949-10 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Enterprise Manager enables users to manage their applications from top to bottom - from monitoring service levels to proactively isolating business exceptions before they escalate to addressing issues at any level in the IT stack. Users can manage the entire application lifecycle with comprehensive application quality management and compliance solutions.
This chapter describes the key features of Enterprise Manager:
Enterprise Manager provides comprehensive, flexible, easy-to-use monitoring functionality that supports the timely detection and notification of impending IT problems across your enterprise. For applications built on Oracle, Enterprise Manager offers the most comprehensive monitoring of the Oracle Grid environment - from Oracle Database instances to Oracle Real Application Clusters to Oracle Application Server Farms and Clusters.
For example, Enterprise Manager's monitoring functionality is tightly integrated with Oracle Database 10g manageability features such as server-generated alerts. These alerts are generated by the database itself about problems it has self-detected. Server-generated alerts can be managed from the Enterprise Manager console and include recommendations on how problems can be resolved. Performance problems such as poorly performing SQL and corresponding recommendations that are generated by the database's self-diagnostic engine, called Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor (ADDM), are also captured and exposed through the Enterprise Manager console. This allows Enterprise Manager administrators to implement ADDM recommendations with ease and convenience.
Enterprise Manager comes with a comprehensive set of performance and health metrics that allow monitoring of key components in your environment such as applications, application servers, databases, as well as the back-end components on which they rely, such as hosts, operating systems and storage.
The Management Agent on each monitored host monitors the status, health, and performance of all managed components (also referred to as targets) on that host. If a target goes down, or if a performance metric crosses a warning or critical threshold, an alert is generated and sent to Enterprise Manager and to Enterprise Manager administrators who have registered interest in receiving such notifications.
Some metrics have predefined limiting parameters called thresholds that cause alerts to be generated when metric values exceed these thresholds. An alert indicates a potential problem indicating that a warning or critical threshold for a monitored metric has been crossed. An alert can also be generated for various availability states such as:
Target is down.
Oracle Management Agent monitoring the target is unreachable.
When an alert is generated, you can access details about the alert from the Enterprise Manager console. Administrators can be automatically notified when an alert is generated, and corrective actions can be automatically set up to resolve an alert condition.
Corrective actions allow you to specify automated responses to alerts. They ensure that routine responses are automatically executed, thereby saving administrators time and ensuring problems are dealt with before they noticeably impact users.
All monitoring information is accessed via the Enterprise Manager console, providing quick views into the health of your monitored environment.
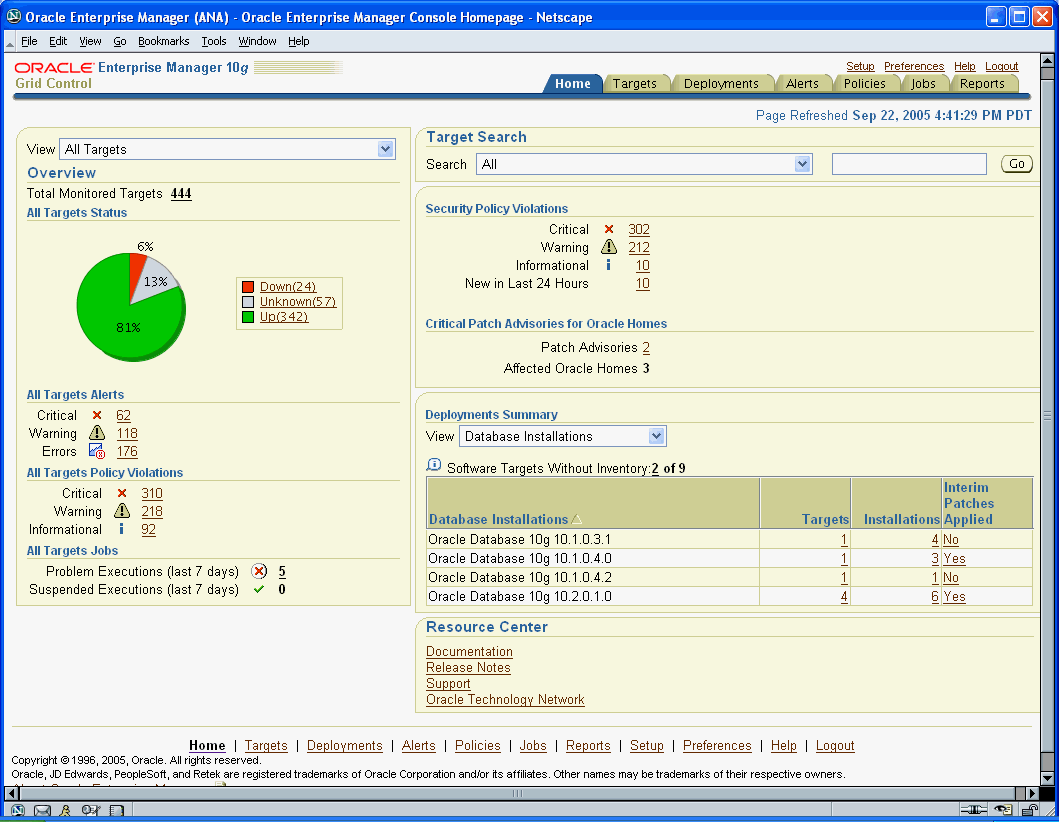
The Enterprise Manager console home page shown in the figure below gives you an at-a-glance view of the overall status of your monitored environment. As shown in the following figure, the home page summarizes key monitoring areas such as availability across all managed targets, open alerts, policy violations, and recent problems with job executions. Links on this page allow you to drill down to detailed performance information.
The Resource Center is your central access point to Enterprise Manager documentation as well as the comprehensive technical resources of the Oracle Technology Network (OTN).
Today's IT operations staff are often responsible for managing a great number of components, such as databases, application servers, hosts, or other components. The Enterprise Manager Group Management System lets you combine components (called targets in Enterprise Manager) into logical sets, called groups. By organizing targets into groups, you can manage and monitor many components as one. The group management system enables you to organize, manage, and effectively monitor the potentially large number of targets in your enterprise.
The group management system allows you to:
View a summary status of the targets within the group.
Monitor outstanding alerts and policy violations for the group collectively, rather than individually.
Monitor the overall performance of the group through performance charts.
Perform administrative tasks, such as scheduling jobs for the entire group, or blacking out the group for maintenance periods.
The Enterprise Manager Job System provides the capacity to automate routine administrative tasks and synchronize components in your environment so you can manage them more efficiently. A job is a unit of work that you define to automate commonly-run tasks. One of the advantages of jobs is that you can schedule a job to start immediately or start at a later date and time. You have the option to have the job run once or at a specific interval.
The Enterprise Manager Job System serves a dual purpose:
Provides for the automation of many administrative tasks, for example, backup, cloning, and patching
Allows users to create their own jobs using their own custom OS and SQL scripts
Enterprise Manager provides predefined job tasks for database targets and deployments. A job task is used to contain predefined, unchangeable logic—for example, patch an application, back up a database, and so on. In addition to predefined job tasks, you can define your own job tasks by writing code to be included in OS and SQL scripts. In addition to submitting jobs to individual targets, you can submit jobs against a group of targets. Any job that you submit to a group is automatically extended to all its member targets and takes into account the membership of the group as it changes.
Information Publisher, Enterprise Manager's powerful reporting framework, makes information about your managed environment available to audiences across the enterprise. Reports are used to present a view of enterprise monitoring information for business intelligence purposes, but can also serve an administrative role by showing activity, resource utilization, and configuration of managed targets. IT managers can use reports to show availability of sets of managed systems. Executives can view reports on availability of applications (such as corporate email) over a period of time.
The reporting framework allows you to create and publish customized reports. Intuitive HTML-based reports can be published via the Web, stored, or e-mailed to selected recipients. Information Publisher comes with a comprehensive library of predefined reports that allow you to generate reports out-of-box without additional setup and configuration. The key benefits of using Information Publisher are:
Provides a framework for creating content-rich, well-formatted HTML reports based on Management Repository data.
Out-of-box reports let you start generating reports immediately without any system configuration or setup.
Ability to schedule automatic generation of reports and store scheduled copies and/or e-mail them to intended audiences.
Ability for Enterprise Manager administrators to share reports with the entire business community: executives, customers, and other Enterprise Manager administrators.
Information Publisher provides you with a feature-rich framework that is your central information source for your enterprise.
To have your enterprise run efficiently, it must adhere to standards that promote the best practices for security, configuration, and storage. Once these standards are developed, you can apply and test for these standards throughout your organization; that is, test for compliance. Compliance in this context is the conformance to standards, or requirements, or both.
Using Enterprise Manager, you can test the conformance of your targets for security standards, and configuration and storage requirements. By continually testing your systems, services, and targets, you are ensuring the best possible protection and performance for your system.
Enterprise Manager provides two types of compliance management: policies and policy groups. Together these define the optimal configurations of systems.
Policies and policy groups are similar in purpose, that is, they both provide rules against which managed entities are evaluated. However, there are differences:
Rules within a policy group are managed as a set. They are viewed, maintained, evaluated, and reported, in the context of a policy group.
Policies are evaluated as a set. Policies are viewed, maintained, and evaluated as standalone entities. Out-of-box policies and user-defined policies are available.
Whether you use the out-of-box policies and policy groups or customize policies and policy groups to meet your particular system requirements, any deviations to your systems or applications are reported. Examples of deviations include inappropriate settings and incorrect system configurations. Using the Information Publisher feature, you can view reports of any policy violations and policy group reports.
Enterprise Manager allows you to monitor and manage a variety of components out-of-the-box.
Enterprise environments consist of a wide variety of components: OS platforms, hardware, software, network, and storage devices. All of these components work in concert to deliver critical information and functionality required to keep enterprise operations performing optimally and providing information to make important business decisions. While Oracle Enterprise Manager allows you to monitor and manage a variety of components out-of-box, you may want to monitor third party components or custom applications specific to your environment.
In addition, you can use the same mechanism used by Oracle and its partners to extend Enterprise Manager to monitor custom components via modular Management Plug-ins. The Management Plug-ins allow you to seamlessly monitor and manage non-Oracle components from the Grid Control console by providing an easy way to specify new classes of components for Enterprise Manager to monitor. Once you have created the new Management Plug-in, you can use the Enterprise Manager console to deploy the new plug-in throughout your enterprise.
Extending Enterprise Manager for monitoring additional components provides the following benefits:
Centralize management information in a single console: When deployed, components defined by the Management Plug-in automatically appear in the Grid Control console. Being able to monitor all targets in your environment provides a consolidated view of your entire enterprise, thus allowing you to monitor and manage all components from a central point.
Extend Enterprise Manager's monitoring and management features to non-Oracle components: Newly added components automatically inherit Enterprise Manager's powerful monitoring and management features, such as: alerts, policies, blackouts, monitoring templates, groups/systems, configuration management, and enterprise reporting.
Comprehensive Service-Level Management: By managing all of your enterprise components with Enterprise Manager, you can more fully utilize the Service-Level Management features offered in Enterprise Manager.
Tip:
For more details, see http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/oem/extensions/index.htmlEnterprise Manager can monitor, administer, maintain, and manage different types of targets. For more details on these targets, refer to the following chapters: