| Oracle® XML DB Developer's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14259-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® XML DB Developer's Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14259-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes the use of the APIs for XMLType in PL/SQL.
This chapter contains these topics:
This chapter describes the PL/SQL Application Program Interfaces (APIs) for XMLType. These include the following:
PL/SQL Document Object Model (DOM) API for XMLType (package DBMS_XMLDOM): For accessing XMLType objects. You can access both XML schema-based and non-schema-based documents. Before database startup, you must specify the read-from and write-to directories in the initialization.ORA file; for example:
UTL_FILE_DIR=/mypath/insidemypath
The read-from and write-to files must be on the server file system.
DOM is an in-memory tree-based object representation of an XML document that enables programmatic access to its elements and attributes. The DOM object and its interface is a W3C recommendation. It specifies the Document Object Model of an XML document including APIs for programmatic access. DOM views the parsed document as a tree of objects.
PL/SQL XML Parser API for XMLType (package DBMS_XMLPARSER): For accessing the contents and structure of XML documents.
PL/SQL XSLT Processor for XMLType (package DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR): For transforming XML documents to other formats using XSLT.
The PL/SQL APIs for XMLType allow you to perform the following tasks:
Create XMLType tables, columns, and views
Construct XMLType instances from data encoded in different character sets.
Access XMLType data
Manipulate XMLType data
See Also:
"Oracle XML DB Features", for an overview of the Oracle XML DB architecture and new features.
Because XMLType provides an in-memory or virtual Document Object Model (DOM), it can use a memory conserving process called lazy XML loading, also sometimes referred to as lazy manifestation. This process optimizes memory usage by only loading rows of data when they are requested. It throws away previously-referenced sections of the document if memory usage grows too large. Lazy XML loading supports highly scalable applications that have many concurrent users needing to access large XML documents.
The XMLType datatype includes support for XML schemas. You can create an XML schema and annotate it with mappings from XML to object-relational storage. To take advantage of the PL/SQL DOM API, first create an XML schema and register it. Then, when you create XMLType tables and columns, you can specify that these conform to the registered XML schema.
XMLType instances can be created from data encoded in any Oracle-supported character set by using the PL/SQL XMLType constructor or XMLType method createXML(). The source XML data must be supplied using datatype BFILE or BLOB. The encoding of the data is specified through argument csid. When this argument is zero (0), the encoding of the source data is determined from the XML prolog, as specified in Appendix F of the XML 1.0 Reference.
Method getBlobVal() retrieves the XML contents in the requested character set.
Caution:
AL32UTF8 is the Oracle Database character set that is appropriate forXMLType data. It is equivalent to the IANA registered standard UTF-8 encoding, which supports all valid XML characters.
Do not confuse Oracle Database database character set UTF8 (no hyphen) with database character set AL32UTF8 or with character encoding UTF-8. Database character set UTF8 has been superseded by AL32UTF8. Do not use UTF8 for XML data. UTF8 supports only Unicode version 3.1 and earlier; it does not support all valid XML characters. AL32UTF8 has no such limitation.
Using database character set UTF8 for XML data could potentially stop a system or affect security negatively. If a character that is not supported by the database character set appears in an input-document element name, a replacement character (usually "?") will be substituted for it. This will terminate parsing and raise an exception. It could cause a fatal error.
This section describes the PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType, DBMS_XMLDOM.
Skip this section if you are familiar with the generic DOM specifications recommended by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
The Document Object Model (DOM) recommended by the W3C is a universal API for accessing the structure of XML documents. It was originally developed to formalize Dynamic HTML, which allows animation, interaction, and dynamic updating of Web pages. DOM provides a language-neutral and platform-neutral object model for Web pages and XML document structures. DOM describes language-independent and platform-independent interfaces to access and operate on XML components and elements. It expresses the structure of an XML document in a universal, content-neutral way. Applications can be written to dynamically delete, add, and edit the content, attributes, and style of XML documents. DOM makes it possible to create applications that work properly on all browsers, servers, and platforms.
Oracle XML Developer's Kit (Oracle XDK) extends the W3C DOM API in various ways. All of these extensions are supported by Oracle XML DB except those relating to client-side operations that are not applicable in the database. This type of procedural processing is available through the SAX interface in the Oracle XDK Java and C components.
All Oracle XML DB APIs for accessing and manipulating XML comply with standard XML processing requirements as approved by the W3C. The PL/SQL DOM supports Levels 1 and 2 from the W3C DOM specifications.
In Oracle9i release 1 (9.0.1), Oracle XDK for PL/SQL implemented DOM Level 1.0 and parts of DOM Level 2.0.
In Oracle9i release 2 (9.2) and Oracle Database 10g release 1 (10.1), the PL/SQL API for XMLType implements DOM Levels 1.0 and Level 2.0 Core, and is fully integrated in the database through extensions to the XMLType API.
The following briefly describes each level:
DOM Level 1.0 – The first formal Level of the DOM specifications, completed in October 1998. Level 1.0 defines support for XML 1.0 and HTML.
DOM Level 2.0 – Completed in November 2000, Level 2.0 extends Level 1.0 with support for XML 1.0 with namespaces and adds support for Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and events (user-interface events and tree manipulation events), and enhances tree manipulations (tree ranges and traversal mechanisms). CSS are a simple mechanism for adding style (fonts, colors, spacing, and so on) to Web documents.
The generic APIs for XML can be classified in two main categories:
Tree-based. DOM is the primary generic tree-based API for XML.
Event-based. SAX (Simple API for XML) is the primary generic event-based programming interface between an XML parser and an XML application.
DOM works by creating objects. These objects have child objects and properties, and the child objects have child objects and properties, and so on. Objects are referenced either by moving down the object hierarchy or by explicitly giving an HTML element an ID attribute. For example:
<img src="employee_jdoe.gif" ID="0123jdoe">
Examples of structural manipulations are:
Reordering elements
Adding or deleting elements
Adding or deleting attributes
Renaming elements
Oracle XML DB extends the Oracle Database XML development platform beyond SQL support for storage and retrieval of XML data. It lets you operate on XMLType instances using DOM in PL/SQL, Java, and C.
The default action for the PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType (DBMS_XMLDOM) is to do the following:
Produce a parse tree that can be accessed by DOM APIs.
Validate, if a DTD is found; otherwise, do not validate.
Raise an application error if parsing fails.
DTD validation occurs when the object document is manifested. If lazy manifestation is employed, then the document is validated when it is used.
The PL/SQL DOM API exploits a C-based representation of XML in the server and operates on XML schema-based XML instances. The PL/SQL, Java, and C DOM APIs for XMLType comply with the W3C DOM Recommendations to define and implement structured storage of XML in relational or object-relational columns and as in-memory instances of XMLType. See "Using PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType: Preparing XML Data", for a description of W3C DOM Recommendations.
The PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType supports XML schema. Oracle XML DB uses annotations within an XML schema as metadata to determine the structure of an XML document structure and the mapping of the document to a database schema.
Note:
For backward compatibility and flexibility, the PL/SQL DOM supports both XML schema-based documents and non-schema-based documents.After an XML schema is registered with Oracle XML DB, the PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType builds an in-memory tree representation of an associated XML document as a hierarchy of node objects, each with its own specialized interfaces. Most node object types can have child node types, which in turn implement additional, more specialized interfaces. Nodes of some node types can have child nodes of various types, while nodes of other node types must be leaf nodes, which do not have child nodes.
Oracle XML DB uses DOM to provide a standard way to translate data between XML and multiple back-end data sources. This eliminates the need to use separate XML translation techniques for the different data sources in your environment. Applications needing to exchange XML data can use a single native XML database to cache XML documents. Oracle XML DB can thus speed up application performance by acting as an intermediate cache between your Web applications and your back-end data sources, whether they are in relational databases or file systems.
See Also:
Chapter 13, "Java API for XMLType"When you build applications based on Oracle XML DB, you do not need the additional components in Oracle XDK. However, you can use Oracle XDK components with Oracle XML DB to deploy a full suite of XML-enabled applications that run end-to-end. You can use features in Oracle XDK for:
Simple API for XML (SAX) interface processing. SAX is an XML standard interface provided by XML parsers and used by procedural and event-based applications.
DOM interface processing, for structural and recursive object-based processing.
Oracle XDK contain the basic building blocks for creating applications that run on a client, in a browser or a plug-in. Such applications typically read, manipulate, transform and view XML documents. To provide a broad variety of deployment options, Oracle XDK is available for Java, C, and C++. Oracle XDK is fully supported and comes with a commercial redistribution license.
Oracle XDK for Java consists of these components:
XML Parsers – Creates and parses XML using industry standard DOM and SAX interfaces. Supports Java, C, C++, and JAXP.
XSL Processor – Transforms or renders XML into other text-based formats such as HTML. Supports Java, C, and C++.
XML Schema Processor – Allows use of XML simple and complex datatypes. Supports Java, C, and C++.
XML Class Generator, Oracle JAXB Class Generator – Automatically generate C++ and Java classes, respectively, from DTDs and XML schemas, to send XML data from Web forms or applications. Class generators accept an input file and create a set of output classes that have corresponding functionality. In the case of the XML Class Generator, the input file is a DTD, and the output is a series of classes that can be used to create XML documents conforming with the DTD.
XML SQL Utility – Generates XML documents, DTDs, and XML schemas from SQL queries. Supports Java.
TransX Utility – Loads data encapsulated in XML into the database. Has additional functionality useful for installations.
XSQL Servlet – Combines XML, SQL, and XSLT in the server to deliver dynamic web content.
XML Pipeline Processor – Invokes Java processes through XML control files.
XSLT VM and Compiler – Provides a high-performance C-based XSLT transformation engine that uses compiled style sheets.
XML Java Beans – Parses, transforms, compares, retrieves, and compresses XML documents using Java components.
To prepare data for using PL/SQL DOM APIs in Oracle XML DB:
Create a standard XML schema.
Annotate the XML schema with definitions for the SQL objects you use.
Register the XML schema, to generate the necessary database mappings.
You can then do any of the following:
Use XMLType views to wrap existing relational or object-relational data in XML formats, making it available to your applications in XML form. See "Wrapping Existing Data into XML with XMLType Views".
Insert XML data into XMLType columns.
Use Oracle XML DB DOM PL/SQL and Java APIs to manipulate XML data stored in XMLType columns and tables.
An XML schema must be registered before it can be referenced by an XML document. When you register an XML schema, elements and attributes it declares are mapped to attributes of corresponding SQL object types within the database.
After XML schema registration, XML documents that conform to the XML schema and reference it can be managed by Oracle XML DB. Tables and columns for storing the conforming documents can be created for root elements defined by the XML schema.
An XML schema is registered by using PL/SQL package DBMS_XMLSCHEMA and by specifying the schema document and its schema-location URL. This URL is a name that uniquely identifies the registered schema within the database; it need not correspond to any real location — in particular, it need not indicate where the schema document is located.
The target namespace of the schema is another URL used in the XML schema. It specifies a namespace for the XML-schema elements and types. An XML document should specify both the namespace of the root element and the schema-location URL identifying the schema that defines this element.
When documents are inserted into Oracle XML DB using path-based protocols such as HTTP(S) and FTP, the XML schema to which the document conforms is registered implicitly, provided its name and location are specified and it has not yet been registered.
Elements and attributes declared within the XML schema get mapped to separate attributes of the corresponding SQL object type. Other information encoded in an XML document, such as comments, processing instructions, namespace declarations and prefixe definitions, and whitespace, is not represented directly.
To store this additional information, binary attribute SYS_XDBPD$ is present in all generated SQL object types. This database attribute stores all information in the original XML document that is not stored using the other database attributes. Retaining this accessory information ensures DOM fidelity for XML documents stored in Oracle XML DB: an XML document retrieved from the database is identical to the original document that was stored.
Note:
In this book, theSYS_XDBPD$ attribute has been omitted from most examples, for simplicity. However, the attribute is always present in SQL object types generated by schema registration.To make existing relational and object-relational data available to your XML applications, you can create XMLType views, wrapping the data in an XML format. You can then accesse this XML data using the PL/SQL DOM API.
After you register an XML schema containing annotations that represent the mapping between XML types and SQL object types, you can create an XMLType view that conforms to the XML schema.
See Also:
Chapter 18, "XMLType Views"All DBMS_XMLDOM methods are supported by Oracle XML DB, with the exception of the following:
writeExternalDTDToFile()
writeExternalDTDToBuffer()
writeExternalDTDToClob()
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for descriptions of the individualDBMS_XMLDOM methodsIn the DOM specification, the term "document" is used to describe a container for many different kinds of information or data, which the DOM objectifies. The DOM specifies the way elements within an XML document container are used to create an object-based tree structure and to define and expose interfaces to manage and use the objects stored in XML documents. Additionally, the DOM supports storage of documents in diverse systems.
When a request such as getNodeType(myNode) is given, it returns myNodeType, which is the node type supported by the parent node. These constants represent the different types that a node can adopt:
ELEMENT_NODE
ATTRIBUTE_NODE
TEXT_NODE
CDATA_SECTION_NODE
ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE
ENTITY_NODE
PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE
COMMENT_NODE
DOCUMENT_NODE
DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE
DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE
NOTATION_NODE
Table 11-1 shows the node types for XML and HTML and the allowed corresponding children node types.
Table 11-1 XML and HTML DOM Node Types and Their Child Node Types
| Node Type | Children Node Types |
|---|---|
Document |
|
DocumentFragment |
|
DocumentType |
No children |
EntityReference |
|
Element |
|
Attr |
|
ProcessingInstruction |
No children |
Comment |
No children |
Text |
No children |
CDATASection |
No children |
Entity |
|
Notation |
No children |
Oracle XML DB DOM API for XMLType also specifies these interfaces:
A NodeList interface to handle ordered lists of Nodes, for example:
The children of a Node
Elements returned by the getElementsByTagName method of the element interface
A NamedNodeMap interface to handle unordered sets of nodes, referenced by their name attribute, such as the attributes of an element.
Oracle Database has several extensions for character-set conversion and input and output to and from a file system. PL/SQL API for XMLType is optimized to operate on XML schema-based XML instances. Function newDOMDocument() constructs a DOM document handle, given an XMLType value.
A typical usage scenario would be for a PL/SQL application to:
Fetch or construct an XMLType instance
Construct a DOMDocument node over the XMLType instance
Use the DOM API to access and manipulate the XML data
Note:
ForDOMDocument, node types represent handles to XML fragments but do not represent the data itself.
For example, if you copy a node value, DOMDocument clones the handle to the same underlying data. Any data modified by one of the handles is visible when accessed by the other handle. The XMLType value from which the DOMDocument handle is constructed is the actual data, and reflects the results of all DOM operations on it.
NodeList and NamedNodeMap objects in the DOM are active; that is, changes to the underlying document structure are reflected in all relevant NodeList and NamedNodeMap objects.
For example, if a DOM user gets a NodeList object containing the children of an element, and then subsequently adds more children to that element (or removes children, or modifies them), then those changes are automatically propagated in the NodeList, without additional action from the user. Likewise, changes to a node in the tree are propagated throughout all references to that node in NodeList and NamedNodeMap objects.
The interfaces: Text, Comment, and CDATASection, all inherit from the CharacterData interface.
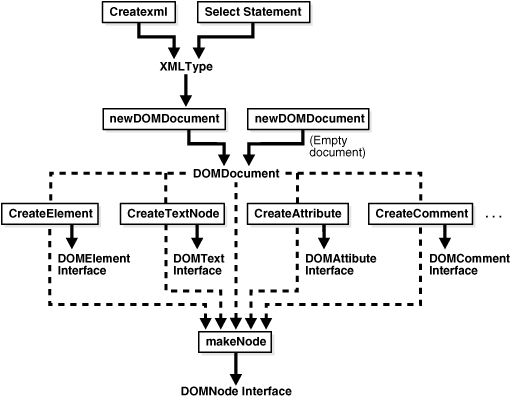
Figure 11-1 illustrates how you use PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType (DBMS_XMLDOM).
You can create a DOM document (DOMDocument) from an existing XMLType or as an empty document.
The newDOMDocument procedure processes the XMLType instance or empty document. This creates a DOMDocument instance.
You can use DOM API methods such as createElement, createText, createAttribute, and createComment to traverse and extend the DOM tree.
The results of methods such as DOMElement and DOMText can also be passed to makeNode to obtain the DOMNode interface.
Figure 11-1 Using PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType
This section presents examples of using the PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType.
Remember to call procedure freeDocument for each DOMDocument instance, when you are through with the instance. You can still access XMLType instances on which DOMDocument instances were built, even after the DOMDocuments have been freed.
Example 11-1 Creating and Manipulating a DOM Document
This example creates a hierarchical, in-memory representation of an XML document – a DOM document. It uses a handle to this DOM document to manipulate it: print it, change part of it, and print it again after the change. Manipulating the DOM document by its handle also indirectly affects the XML data represented by the document, so that querying that data after the change shows the changed result.
The in-memory document is created from an XMLType variable using PL/SQL function newDOMDocument. The handle to this document is created using function makeNode. The document is written to a VARCHAR2 buffer using function writeToBuffer, and the buffer is printed using DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line.
After manipulating the document using various DBMS_XMLDOM procedures, the (changed) data in the XMLType variable is inserted into a table and queried, showing the change. It is only when the data is inserted into a database table that it becomes persistent; until then, it exists in memory only. This persistence is demonstrated by the fact that the database query is made after the in-memory document (DOMDocument instance) has been freed.
CREATE TABLE person OF XMLType;
DECLARE
var XMLType;
doc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocument;
ndoc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode;
docelem DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMElement;
node DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode;
childnode DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode;
nodelist DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNodelist;
buf VARCHAR2(2000);
BEGIN
var := XMLType('<PERSON><NAME>ramesh</NAME></PERSON>');
-- Create DOMDocument handle
doc := DBMS_XMLDOM.newDOMDocument(var);
ndoc := DBMS_XMLDOM.makeNode(doc);
DBMS_XMLDOM.writeToBuffer(ndoc, buf);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('Before:'||buf);
docelem := DBMS_XMLDOM.getDocumentElement(doc);
-- Access element
nodelist := DBMS_XMLDOM.getElementsByTagName(docelem, 'NAME');
node := DBMS_XMLDOM.item(nodelist, 0);
childnode := DBMS_XMLDOM.getFirstChild(node);
-- Manipulate element
DBMS_XMLDOM.setNodeValue(childnode, 'raj');
DBMS_XMLDOM.writeToBuffer(ndoc, buf);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('After:'||buf);
DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocument(doc);
INSERT INTO person VALUES (var);
END;
/
This produces the following output:
Before:<PERSON> <NAME>ramesh</NAME> </PERSON> After:<PERSON> <NAME>raj</NAME> </PERSON>
This query confirms that the data has changed:
SELECT * FROM person;
SYS_NC_ROWINFO$
---------------
<PERSON>
<NAME>raj</NAME>
</PERSON>
1 row selected.
Example 11-2 Creating an Element Node and Obtaining Information About It
This example creates an empty DOM document, and then adds an element node (<ELEM>) to the document. DMBS_XMLDOM API node procedures are used to obtain the name (<ELEM>), value (NULL), and type (1 = element node) of the element node.
DECLARE
doc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocument;
elem DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMElement;
nelem DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode;
BEGIN
doc := DBMS_XMLDOM.newDOMDocument;
elem := DBMS_XMLDOM.createElement(doc, 'ELEM');
nelem := DBMS_XMLDOM.makeNode(elem);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('Node name = ' || DBMS_XMLDOM.getNodeName(nelem));
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('Node value = '|| DBMS_XMLDOM.getNodeValue(nelem));
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line('Node type = ' || DBMS_XMLDOM.getNodeType(nelem));
DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocument(doc);
END;
/
This produces the following output:
Node name = ELEM Node value = Node type = 1
XML documents are made up of storage units, called entities, that contain either parsed or unparsed data. Parsed data is made up of characters, some of which form character data and some of which form markup. Markup encodes a description of the document storage layout and logical structure. XML provides a mechanism for imposing constraints on the storage layout and logical structure.
A software module called an XML parser or processor reads XML documents and provides access to their content and structure. An XML parser usually does its work on behalf of another module, typically the application.
The PL/SQL Parser API for XMLType (DBMS_XMLPARSER) builds a result tree that can be accessed by PL/SQL APIs. If parsing fails, it raises an error.
See Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for descriptions of the individual methods of the PL/SQL Parser API for XMLType (DBMS_XMLPARSER).
The following DBMS_XMLPARSER methods are not supported:
parseDTD()
parseDTDBuffer()
parseDTDClob()
setDocType()
setErrorLog()
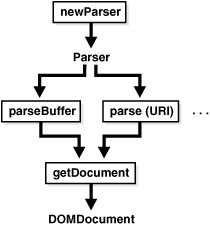
Figure 11-2 illustrates how to use the PL/SQL Parser for XMLType (DBMS_XMLPARSER). These are the steps:
Construct a parser instance using method.
Parse XML documents using methods such as parseBuffer, parseClob, and parse(URI). An error is raised if the input is not a valid XML document.
Call getDocument on the parser to obtain a DOMDocument interface.
Figure 11-2 Using PL/SQL Parser API for XMLType
Example 11-3 Parsing an XML Document
This example parses a simple XML document. It creates an XML parser (instance of DBMS_XMLPARSER.parser) and uses it to parse the XML document (text) in variable indoc. Parsing creates a DOM document, which is retrieved from the parser using DBMS_XMLPARSER.getDocument. A DOM node is created that contains the entire document, and the node is printed. After freeing (destroying) the DOM document, the parser instance is freed using DBMS_XMLPARSER.freeParser.
DECLARE indoc VARCHAR2(2000); indomdoc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocument; innode DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode; myparser DBMS_XMLPARSER.parser; buf VARCHAR2(2000); BEGIN indoc := '<emp><name>De Selby</name></emp>'; myParser := DBMS_XMLPARSER.newParser; DBMS_XMLPARSER.parseBuffer(myParser, indoc); indomdoc := DBMS_XMLPARSER.getDocument(myParser); innode := DBMS_XMLDOM.makeNode(indomdoc); DBMS_XMLDOM.writeToBuffer(innode, buf); DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line(buf); DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocument(indomdoc); DBMS_XMLPARSER.freeParser(myParser); END; /
This produces the following output:
<emp><name>De Selby</name></emp>
W3C XSL Recommendation describes rules for transforming a source tree into a result tree. A transformation expressed in Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT) language is called an XSL style sheet. The transformation specified is achieved by associating patterns with templates defined in the XSLT style sheet. A template is instantiated to create part of the result tree.
The Oracle XML DB PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType also supports Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT). This enables transformation from one XML document to another, or conversion into HTML, PDF, or other formats. XSLT is also widely used to convert XML to HTML for browser display.
The embedded XSLT processor follows Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) statements and traverses the DOM tree structure for XML data residing in XMLType. Oracle XML DB applications do not require a separate parser as did the prior release XML Parser for PL/SQL. However, applications requiring external processing can still use the XML Parser for PL/SQL first to expose the document structure.
PL/SQL package DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR provides a convenient and efficient way of applying a single style sheet to multiple documents. The performance of this package is better than that of transform() because the style sheet is parsed only once.
Note:
The XML Parser for PL/SQL in Oracle XDK parses an XML document (or a standalone DTD) so that the XML document can be processed by an application, typically running on the client. PL/SQL APIs forXMLType are used for applications that run on the server and are natively integrated in the database. Benefits include performance improvements and enhanced access and manipulation options.PL/SQL XSLT Processor for XMLType (DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR) is the Oracle XML DB implementation of the XSL processor. This follows the W3C XSLT final recommendation (REC-xslt-19991116). It includes the required action of an XSL processor in terms of how it must read XSLT style sheets and the transformations it must achieve.
The types and methods of the PL/SQL XSLT Processor API are made available by the PL/SQL package, DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR. The methods in this package use two PL/SQL datatypes specific to the XSL Processor implementation: PROCESSOR and STYLESHEET .
All DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR methods are supported by Oracle XML DB, with the exception of method setErrorLog().
See Also:
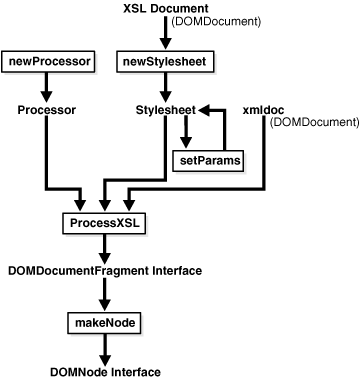
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for descriptions of the individualDBMS_XSLPROCESSOR methodsFigure 11-3 illustrates how to use XSLT Processor for XMLType (DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR). These are the steps:
Construct an XSLT processor using newProcessor.
Use newStylesheet to build a STYLESHEET object from a DOM document.
Optionally, you can set parameters for the STYLESHEET object using setParams.
Use processXSL to transform a DOM document using the processor and STYLESHEET object.
Use the PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType to manipulate the result of XSLT processing.
Figure 11-3 Using PL/SQL XSLT Processor for XMLType
Example 11-4 Transforming an XML Document Using an XSL Style Sheet
This example transforms an XML document using procedure processXSL. It uses the same parser instance to create two different DOM documents: the XML text to transform and the XSLT style sheet. An XSL processor instance is created, which applies the style sheet to the source XML to produce a new DOM fragment. A DOM node (outnode) is created from this fragment, and the node content is printed. The output DOM fragment, parser, and XSLT processor instances are freed using procedures freeDocFrag, freeParser, and freeProcessor, respectively.
DECLARE
indoc VARCHAR2(2000);
xsldoc VARCHAR2(2000);
myParser DBMS_XMLPARSER.parser;
indomdoc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocument;
xsltdomdoc DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocument;
xsl DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.stylesheet;
outdomdocf DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMDocumentFragment;
outnode DBMS_XMLDOM.DOMNode;
proc DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.processor;
buf VARCHAR2(2000);
BEGIN
indoc := '<emp><empno>1</empno>
<fname>robert</fname>
<lname>smith</lname>
<sal>1000</sal>
<job>engineer</job>
</emp>';
xsldoc := '<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output encoding="utf-8"/>
<!-- alphabetizes an xml tree -->
<xsl:template match="*">
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="*|text()">
<xsl:sort select="name(.)" data-type="text"
order="ascending"/>
</xsl:apply-templates>
</xsl:copy>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="text()">
<xsl:value-of select="normalize-space(.)"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>';
myParser := DBMS_XMLPARSER.newParser;
DBMS_XMLPARSER.parseBuffer(myParser, indoc);
indomdoc := DBMS_XMLPARSER.getDocument(myParser);
DBMS_XMLPARSER.parseBuffer(myParser, xsldoc);
xsltdomdoc := DBMS_XMLPARSER.getDocument(myParser);
xsl := DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.newStyleSheet(xsltdomdoc, '');
proc := DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.newProcessor;
--apply stylesheet to DOM document
outdomdocf := DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.processXSL(proc, xsl, indomdoc);
outnode := DBMS_XMLDOM.makeNode(outdomdocf);
-- PL/SQL DOM API for XMLType can be used here
DBMS_XMLDOM.writeToBuffer(outnode, buf);
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line(buf);
DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocument(indomdoc);
DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocument(xsltdomdoc);
DBMS_XMLDOM.freeDocFrag(outdomdocf);
DBMS_XMLPARSER.freeParser(myParser);
DBMS_XSLPROCESSOR.freeProcessor(proc);
END;
/
This produces the following output:
<emp> <empno>1</empno> <fname>robert</fname> <job>engineer</job> <lname>smith</l name> <sal>1000</sal> </emp>