| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
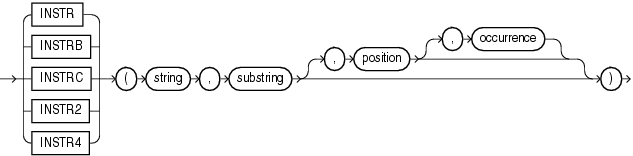
The INSTR functions search string for substring. The function returns an integer indicating the position of the character in string that is the first character of this occurrence. INSTR calculates strings using characters as defined by the input character set. INSTRB uses bytes instead of characters. INSTRC uses Unicode complete characters. INSTR2 uses UCS2 code points. INSTR4 uses UCS4 code points.
position is an nonzero integer indicating the character of string where Oracle Database begins the search. If position is negative, then Oracle counts backward from the end of string and then searches backward from the resulting position.
occurrence is an integer indicating which occurrence of string Oracle should search for. The value of occurrence must be positive.
Both string and substring can be any of the datatypes CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB. The value returned is of NUMBER datatype.
Both position and occurrence must be of datatype NUMBER, or any datatype that can be implicitly converted to NUMBER, and must resolve to an integer. The default values of both position and occurrence are 1, meaning Oracle begins searching at the first character of string for the first occurrence of substring. The return value is relative to the beginning of string, regardless of the value of position, and is expressed in characters. If the search is unsuccessful (if substring does not appear occurrence times after the position character of string), then the return value is 0.
See Also:
Table 2-10, "Implicit Type Conversion Matrix" for more information on implicit conversionThe following example searches the string CORPORATE FLOOR, beginning with the third character, for the string "OR". It returns the position in CORPORATE FLOOR at which the second occurrence of "OR" begins:
SELECT INSTR('CORPORATE FLOOR','OR', 3, 2)
"Instring" FROM DUAL;
Instring
----------
14
In the next example, Oracle counts backward from the last character to the third character from the end, which is the first O in FLOOR. Oracle then searches backward for the second occurrence of OR, and finds that this second occurrence begins with the second character in the search string :
SELECT INSTR('CORPORATE FLOOR','OR', -3, 2)
"Reversed Instring"
FROM DUAL;
Reversed Instring
-----------------
2
The next example assumes a double-byte database character set.
SELECT INSTRB('CORPORATE FLOOR','OR',5,2) "Instring in bytes"
FROM DUAL;
Instring in bytes
-----------------
27