| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the COMMIT statement to end your current transaction and make permanent all changes performed in the transaction. A transaction is a sequence of SQL statements that Oracle Database treats as a single unit. This statement also erases all savepoints in the transaction and releases transaction locks.
Until you commit a transaction:
You can see any changes you have made during the transaction by querying the modified tables, but other users cannot see the changes. After you commit the transaction, the changes are visible to other users' statements that execute after the commit.
You can roll back (undo) any changes made during the transaction with the ROLLBACK statement (see ROLLBACK.
Oracle Database issues an implicit COMMIT before and after any data definition language (DDL) statement.
You can also use this statement to
Commit an in-doubt distributed transaction manually
Terminate a read-only transaction begun by a SET TRANSACTION statement
Oracle recommends that you explicitly end every transaction in your application programs with a COMMIT or ROLLBACK statement, including the last transaction, before disconnecting from Oracle Database. If you do not explicitly commit the transaction and the program terminates abnormally, then the last uncommitted transaction is automatically rolled back.
A normal exit from most Oracle utilities and tools causes the current transaction to be committed. A normal exit from an Oracle precompiler program does not commit the transaction and relies on Oracle Database to roll back the current transaction.
See Also:
Oracle Database Concepts for more information on transactions
SET TRANSACTION for more information on specifying characteristics of a transaction
You need no privileges to commit your current transaction.
To manually commit a distributed in-doubt transaction that you originally committed, you must have FORCE TRANSACTION system privilege. To manually commit a distributed in-doubt transaction that was originally committed by another user, you must have FORCE ANY TRANSACTION system privilege.
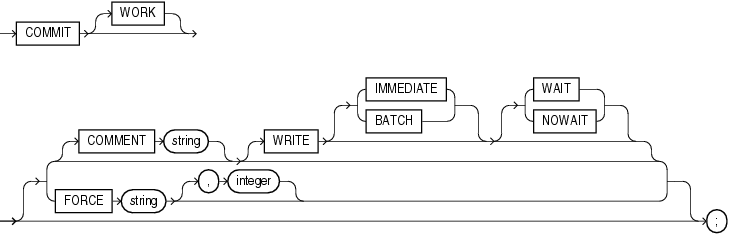
All clauses after the COMMIT keyword are optional. If you specify only COMMIT, then the default is COMMIT WORK WRITE IMMEDIATE WAIT.
The WORK keyword is supported for compliance with standard SQL. The statements COMMIT and COMMIT WORK are equivalent.
Specify a comment to be associated with the current transaction. The 'text' is a quoted literal of up to 255 bytes that Oracle Database stores in the data dictionary view DBA_2PC_PENDING along with the transaction ID if a distributed transaction becomes in doubt. This comment can help you diagnose the failure of a distributed transaction.
See Also:
COMMENT for more information on adding comments to SQL statementsUse this clause to specify the priority with which the redo information generated by the commit operation is written to the redo log. This clause can improve performance by reducing latency, thus eliminating the wait for an I/O to the redo log. Use this clause to improve response time in environments with stringent response time requirements where the following conditions apply:
The volume of update transactions is large, requiring that the redo log be written to disk frequently.
The application can tolerate the loss of an asynchronously committed transaction.
The latency contributed by waiting for the redo log write to occur contributes significantly to overall response time.
Note:
if you omit this clause, then the behavior of the commit operation is controlled by theCOMMIT_WRITE initialization parameter, if it as been set. The default value of the parameter is the same as the default for this clause. Therefore, if the parameter has not been set and you omit this clause, then commit records are written to disk before control is returned to the user.IMMEDIATE The IMMEDIATE parameter initiates I/O, causing the redo for the commit of the transaction to be written out immediately by sending a message to the LGWR process. If you specify neither IMMEDIATE nor BATCH, then IMMEDIATE is the default.
BATCH The BATCH parameter causes the redo to be buffered to the redo log. No I/O is initiated.
WAIT The WAIT parameter ensures that the commit will not return until the corresponding redo is persistent in the online redo log. If you specify neither WAIT nor NOWAIT, then WAIT is the default.
NOWAIT The NOWAIT parameter allows the commit to return before the redo is persistent in the redo log.
See Also:
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for more information on asynchronous commitIn a distributed database system, the FORCE clause lets you manually commit an in-doubt distributed transaction. The transaction is identified by the 'string' containing its local or global transaction ID. To find the IDs of such transactions, query the data dictionary view DBA_2PC_PENDING. You can use integer to specifically assign the transaction a system change number (SCN). If you omit integer, then the transaction is committed using the current SCN.
Note:
ACOMMIT statement with a FORCE clause commits only the specified transaction. Such a statement does not affect your current transaction.See Also:
Oracle Database Heterogeneous Connectivity Administrator's Guide for more information on these topicsCommitting an Insert: Example This statement inserts a row into the hr.regions table and commits this change:
INSERT INTO regions VALUES (5, 'Antarctica'); COMMIT WORK;
To commit the same insert operation and instruct the database to buffer the change to the redo log, without initiating disk I/O, use the following COMMIT statement:
COMMIT WRITE BATCH;
Commenting on COMMIT: Example The following statement commits the current transaction and associates a comment with it:
COMMIT
COMMENT 'In-doubt transaction Code 36, Call (415) 555-2637';
If a network or machine failure prevents this distributed transaction from committing properly, then Oracle Database stores the comment in the data dictionary along with the transaction ID. The comment indicates the part of the application in which the failure occurred and provides information for contacting the administrator of the database where the transaction was committed.
Forcing an In-Doubt Transaction: Example The following statement manually commits an in-doubt distributed transaction:
COMMIT FORCE '22.57.53';