| Oracle® Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14227-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Advanced Replication Management API Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14227-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter illustrates how to manage the replication objects and queues in your replication environment using the replication management API.
This chapter contains these topics:
As your database needs change, you might need to modify the characteristics of your replicated objects. It is important that you do not directly execute DDL to alter your replicated objects. Doing so might cause your replication environment to fail.
Note:
If the logical structure of a master table is altered (for example, if a column name or type is changed), then all dependent materialized views must be rebuilt.Use the ALTER_MASTER_REPOBJECT procedure in the DBMS_REPCAT package to alter the characteristics of your replicated objects in a quiesced master group. From the example following, notice that you simply include the necessary DDL within the procedure call (see the ddl_text parameter).
If any master site is lower than 9.0.1 compatibility level, then you must use the following procedure. That is, the master group must be quiesced to modify a replicated object. You control the compatibility level of a database with the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter.
Meet the following requirements to complete these actions:
Executed As: Replication Administrator
Executed At: Master Definition Site
Replication Status: Quiesced
Complete the following steps to alter a replicated object in a quiesced master group.
Note:
If your master site is running Oracle8i Database release 8.1.7 or later in a single master environment and you are making a safe change to a replicated object, then you might not need to quiesce the master group. See the "ALTER_MASTER_REPOBJECT Procedure" for information about when quiesce is not required.
If you are viewing this document online, then you can copy the text from the "BEGINNING OF SCRIPT" line after this note to the "END OF SCRIPT" line into a text editor and then edit the text to create a script for your environment.
/************************* BEGINNING OF SCRIPT ******************************
Step 1 Connect to the master definition site as the replication administrator.
*/
SET ECHO ON SPOOL alter_rep_object.out CONNECT repadmin/repadmin@orc1.world /*
Step 2 If necessary, then quiesce the master group.
See the "ALTER_MASTER_REPOBJECT Procedure" for information about when quiesce is not required.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.SUSPEND_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; / /*
Step 3 In a separate SQL*Plus session, check the status of the master group you are quiescing.
Do not proceed until the group's status is QUIESCED.
To check the status, run the following query:
SELECT GNAME, STATUS FROM DBA_REPGROUP; */ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue when the master group's status is QUIESCED. /*
Step 4 Alter the replicated object.
*/
BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.ALTER_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( sname => 'hr', oname => 'employees', type => 'TABLE', ddl_text => 'ALTER TABLE hr.employees ADD (timestamp DATE)'); END; / /*
Step 5 Regenerate replication support for the altered object.
*/
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT (
sname => 'hr',
oname => 'employees',
type => 'TABLE',
min_communication => TRUE);
END;
/
/*
Step 6 In a separate SQL*Plus session, check if DBA_REPCATLOG is empty.
Do not proceed until this view is empty.
Execute the following SELECT statement in another SQL*Plus session to monitor the DBA_REPCATLOG view:
SELECT * FROM DBA_REPCATLOG WHERE GNAME = 'HR_REPG'; */ PAUSE Press <RETURN> to continue when DBA_REPCATLOG is empty. /*
Step 7 Resume replication activity.
*/
BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; / SET ECHO OFF SPOOL OFF /************************* END OF SCRIPT **********************************/
You might have a situation in which you need to modify a replicated object, but you do not want this modification replicated to the other sites in the replication environment. For example, you might want to disable replication in the following situations:
When you are using procedural replication to propagate a change, always disable row-level replication at the start of your procedure.
You might need to disable replication in triggers defined on replicated tables to avoid replicating trigger actions multiple times. See "Ensuring that Replicated Triggers Fire Only Once".
Sometimes when you manually resolve a conflict, you might not want to replicate this modification to the other copies of the table.
You might need to do this, for example, if you need to correct the state of a record at one site so that a conflicting replicated update will succeed when you reexecute the error transaction. Or, you might use an unreplicated modification to undo the effects of a transaction at its origin site because the transaction could not be applied at the destination site. In this example, you can use the Replication Management tool to delete the conflicting transaction from the destination site.
To modify tables without replicating the modifications, use the REPLICATION_ON and REPLICATION_OFF procedures in the DBMS_REPUTIL package. These procedures take no arguments and are used as flags by the generated replication triggers.
Note:
To enable and disable replication, you must have theEXECUTE privilege on the DBMS_REPUTIL package.The DBMS_REPUTIL.REPLICATION_OFF procedure sets the state of an internal replication variable for the current session to false. Because all replicated triggers check the state of this variable before queuing any transactions, modifications made to the replicated tables that use row-level replication do not result in any queued deferred transactions.
Caution:
Turning replication on or off affects only the current session. That is, other users currently connected to the same server are not restricted from placing committed changes in the deferred transaction queue.If you are using procedural replication, then call REPLICATION_OFF at the start of your procedure, as shown in the following example. This ensures that the replication facility does not attempt to use row-level replication to propagate the changes that you make.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE update_objects AS PROCEDURE update_emp(adjustment IN NUMBER); END; / CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY update_objects AS PROCEDURE update_emp(adjustment IN NUMBER) IS BEGIN --turn off row-level replication for set update DBMS_REPUTIL.REPLICATION_OFF; UPDATE emp . . .; --reenable replication DBMS_REPUTIL.REPLICATION_ON; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN . . . DBMS_REPUTIL.REPLICATION_ON; END; END; /
After resolving any conflicts, or at the end of your replicated procedure, be certain to call DBMS_REPUTIL.REPLICATION_ON to resume normal replication of changes to your replicated tables or materialized views. This procedure takes no arguments. Calling REPLICATION_ON sets the internal replication variable to true.
If you have defined a replicated trigger on a replicated table, then you might need to ensure that the trigger fires only once for each change that you make. Typically, you only want the trigger to fire when the change is first made, and you do not want the remote trigger to fire when the change is replicated to the remote site.
You should check the value of the DBMS_REPUTIL.FROM_REMOTE package variable at the start of your trigger. The trigger should update the table only if the value of this variable is false.
Alternatively, you can disable replication at the start of the trigger and reenable it at the end of the trigger when modifying rows other than the one that caused the trigger to fire. Using this method, only the original change is replicated to the remote sites. Then the replicated trigger fires at each remote site. Any updates performed by the replicated trigger are not pushed to any other sites.
Using this approach, conflict resolution is not invoked. Therefore, you must ensure that the changes resulting from the trigger do not affect the consistency of the data.
LOB columns can be replicated, but LONG columns cannot be replicated. You can convert the datatype of a LONG column to a CLOB column and the datatype of a LONG_RAW column to a BLOB column.
Converting a LONG column to a LOB column can result in increased network bandwidth requirements because the data in such a column is replicated after conversion. Make sure you have adequate network bandwidth before completing the procedure in this section.
See Also:
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Large Objects for more information about applications andLONG to LOB conversionComplete the following steps to convert a LONG column to a LOB column in a replicated table:
Step 1 Make sure the data in the LONG column is consistent at all replication sites.
If a table containing a LONG column is configured as a master table, then Oracle does not replicate changes to the data in the LONG column. Therefore, the data in the LONG column might not match at all of your replication sites. You must make sure the data in the LONG column matches at all master sites before proceeding.
Step 2 Connect to the master definition site as the replication administrator.
CONNECT repadmin/repadmin@orc1.world
Step 3 If the replication status is normal, then change the status to quiesced.
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.SUSPEND_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'sales_mg'); END; /
Step 4 Convert the LONG column to a LOB column.
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.ALTER_MASTER_REPOBJECT ( sname => 'staff', oname => 'positions', type => 'TABLE', ddl_text => 'ALTER TABLE staff.positions MODIFY (job_desc CLOB)'); END; /
A LONG_RAW column can be converted to a BLOB column using a similar ALTER TABLE statement.
Step 5 Regenerate replication support for the altered master table.
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.GENERATE_REPLICATION_SUPPORT ( sname => 'staff', oname => 'positions', type => 'TABLE', min_communication => TRUE); END; /
BEGIN
DBMS_REPCAT.RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'sales_mg'); END; /
Step 7 If materialized views are based on the altered table at any of the master sites, then rebuild these materialized views.
Rebuild materialized views if necessary.
It is possible for the differences to arise in replicated tables. When administering a replication environment, you might want to check, periodically, whether the contents of two replicated tables are identical. The following procedures in the DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF package let you identify, and optionally rectify, the differences between two tables.
The DIFFERENCES procedure compares two replicas of a table, and determines all rows in the first replica that are not in the second and all rows in the second that are not in the first. The output of this procedure is stored in two user-created tables. The first table stores the values of the missing rows, and the second table is used to indicate which site contains each row.
The RECTIFY procedure uses the information generated by the DIFFERENCES procedure to rectify the two tables. Any rows found in the first table and not in the second are inserted into the second table. Any rows found in the second table and not in the first are deleted from the second table.
To restore equivalency between all copies of a replicated table, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Select one copy of the table to be the "reference" table.
This copy will be used to update all other replicas of the table as needed.
Step 2 Determine if it is necessary to check all rows and columns in the table for differences, or only a subset.
For example, it might not be necessary to check rows that have not been updated since the last time that you checked for differences. Although it is not necessary to check all columns, your column list must include all columns that make up the primary key (or that you designated as a substitute identity key) for the table.
Step 3 After determining which columns you will be checking in the table, create two tables to hold the results of the comparison.
You must create one table that can hold the data for the columns being compared. For example, if you decide to compare the employee_id, salary, and department_id columns of the employees table, then your CREATE statement would need to be similar to the following:
CREATE TABLE hr.missing_rows_data ( employee_id NUMBER(6), salary NUMBER(8,2), department_id NUMBER(4));
You must also create a table that indicates where the row is found. This table must contain three columns with the datatypes shown in the following example:
CREATE TABLE hr.missing_rows_location ( present VARCHAR2(128), absent VARCHAR2(128), r_id ROWID);
Step 4 Suspend replication activity for the replication group containing the tables that you want to compare.
Although suspending replication activity for the group is not a requirement, rectifying tables that were not quiesced first can result in inconsistencies in your data.
CONNECT repadmin/repadmin BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.SUSPEND_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; /
Step 5 At the site containing the "reference" table, call the DIFFERENCES procedure.
For example, if you wanted to compare the employees tables at the New York and San Francisco sites, then your procedure call would look similar to the following:
BEGIN DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.DIFFERENCES ( sname1 => 'hr', oname1 => 'employees', reference_site => 'ny.world', sname2 => 'hr', oname2 => 'employees', comparison_site => 'mv4.world', where_clause => '', column_list => 'employee_id,salary,department_id', missing_rows_sname => 'hr', missing_rows_oname1 => 'missing_rows_data', missing_rows_oname2 => 'missing_rows_location', missing_rows_site => 'ny.world', max_missing => 500, commit_rows => 50); END; /
Figure 9-1 shows an example of two replicas of the employees table and what the resulting missing rows tables would look like if you executed the DIFFERENCES procedure on these replicas.
Figure 9-1 Determining Differences Between Replicas
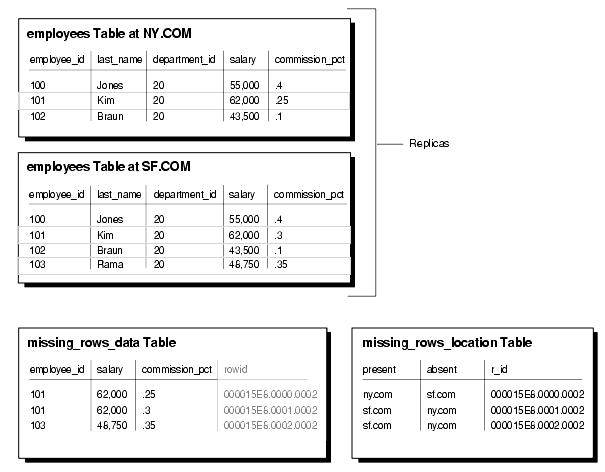
Notice that the two missing rows tables are related by the ROWID and r_id columns.
Step 6 Rectify the table at the "comparison" site to be equivalent to the table at the "reference" site.
BEGIN
DBMS_RECTIFIER_DIFF.RECTIFY ( sname1 => 'hr', oname1 => 'employees', reference_site => 'ny.world', sname2 => 'hr', oname2 => 'employees', comparison_site => 'mv4.world', column_list => 'employee_id,salary,department_id', missing_rows_sname => 'hr', missing_rows_oname1 => 'missing_rows_data', missing_rows_oname2 => 'missing_rows_location', missing_rows_site => 'ny.world', commit_rows => 50); END; /
The RECTIFY procedure temporarily disables replication at the "comparison" site while it performs the necessary insertions and deletions, as you would not want to propagate these changes. RECTIFY first performs all of the necessary DELETE operations and then performs all of the INSERT operations. This ensures that there are no violations of a PRIMARY KEY constraint.
After you have successfully executed the RECTIFY procedure, your missing rows tables should be empty.
Caution:
If you have any additional constraints on the "comparison" table, then you must ensure that they are not violated when you callRECTIFY. You might need to update the table directly using the information in the missing rows table. If so, then be sure to DELETE the appropriate rows from the missing rows tables.Step 7 Repeat Steps 5 and 6 for the remaining copies of the replicated table.
Remember to use the same "reference" table each time to ensure that all copies are identical when you complete this procedure.
Step 8 Resume replication activity for the master group.
BEGIN DBMS_REPCAT.RESUME_MASTER_ACTIVITY ( gname => 'hr_repg'); END; /
Typically, Advanced Replication is configured to push and purge the deferred transaction queue automatically. At times, however, you might need to push or purge the deferred transaction queue manually. The process for pushing the deferred transaction queue is the same at master sites and materialized view sites.
Master sites are configured to push the deferred transaction queue automatically at set intervals. At materialized view sites, if you do not automatically propagate the transactions in your deferred transaction queue during the refresh of your materialized view, then you must complete the following steps to propagate changes made to the updatable materialized view to its master table or master materialized view.
This example illustrates pushing the deferred transaction queue at a materialized view site, but the process is the same at master sites and materialized view sites.
Executed As: Materialized View Administrator
Executed At: Materialized View Site
Complete the following steps:
Step 1 Connect to the materialized view site as the materialized view administrator.
CONNECT mviewadmin/mviewadmin@mv1.world
Step 2 Execute the following SELECT statement to view the deferred transactions and their destinations.
Propagation of the deferred transaction queue is based on the destination of the transaction. Each distinct destination and the number of transactions pending for the destination will be displayed.
SELECT DISTINCT(dblink), COUNT(deferred_tran_id) FROM deftrandest GROUP BY dblink;
Step 3 Execute the DBMS_DEFER_SYS.PUSH function for each site that is listed as a destination for a deferred transaction.
DECLARE temp INTEGER; BEGIN temp := DBMS_DEFER_SYS.PUSH ( destination => 'orc1.world', stop_on_error => FALSE, delay_seconds => 0, parallelism => 0); END; /
Run the PUSH procedure for each destination that was returned in the SELECT statement you ran in Step 2.
If your system is not set to automatically purge the successfully propagated transactions in your deferred transaction queue periodically, then you must complete the following steps to purge them manually.
This example illustrates purging the deferred transaction queue at a materialized view site, but the process is the same at master sites and materialized view sites.
Executed As: Materialized View Administrator
Executed At: Materialized View Site
Complete the following steps:
Step 1 Connect to the materialized view site as the materialized view administrator.
CONNECT mviewadmin/mviewadmin@mv1.world
Step 2 Purge the deferred transaction queue.
DECLARE
temp INTEGER; BEGIN temp := DBMS_DEFER_SYS.PURGE ( purge_method => DBMS_DEFER_SYS.PURGE_METHOD_QUICK); END; /
Note:
If you use thepurge_method_quick parameter, deferred transactions and deferred procedure calls that have been successfully pushed can remain in the DEFTRAN and DEFCALL data dictionary views for longer than expected before they are purged. See the "Usage Notes" for DBMS_DEFER_SYS.PURGE for details.If you are using column objects, collections, or REFs in a replicated table, then you can use the GET_ANYDATA_ARG function in the DBMS_DEFER_QUERY package to determine the value of an argument in a deferred call that involves one of these user-defined types.
The following example illustrates how to use the GET_ANYDATA_ARG function. This example uses the following user-defined types in the oe sample schema.
CREATE TYPE phone_list_typ AS VARRAY(5) OF VARCHAR2(25);
/
CREATE TYPE warehouse_typ AS OBJECT
(warehouse_id NUMBER(3),
warehouse_name VARCHAR2(35),
location_id NUMBER(4)
);
/
CREATE TYPE inventory_typ AS OBJECT
(product_id NUMBER(6),
warehouse warehouse_typ,
quantity_on_hand NUMBER(8)
);
/
CREATE TYPE inventory_list_typ AS TABLE OF inventory_typ;
/
The following procedure retrieves the argument value for collection, object, and REF instances of calls stored in the deferred transactions queue. This procedure assumes that the call number and transaction id are available.
The user who creates the procedure must have EXECUTE privilege on the DBMS_DEFER_QUERY package and must have CREATE PROCEDURE privilege. This example uses the oe sample schema. Therefore, to run the example, you must grant the oe user these privileges.
CONNECT SYSTEM/MANAGER AS SYSDBA
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_DEFER_QUERY TO oe;
GRANT CREATE PROCEDURE TO oe;
CONNECT oe/oe@orc1.world
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE get_userdef_arg AS
call_no NUMBER := 0;
txn_id VARCHAR2(128) := 'xx.xx.xx';
anydata_val ANYDATA;
t ANYTYPE;
data_pl phone_list_typ; -- varray
data_ntt inventory_list_typ; -- nested table type
data_p warehouse_typ; -- object type
ref1 REF inventory_typ; -- REF type
rval PLS_INTEGER; -- return value
tc PLS_INTEGER; -- return value
prec PLS_INTEGER; -- precision
scale PLS_INTEGER; -- scale
len PLS_INTEGER; -- length
csid PLS_INTEGER; -- character set id
csfrm PLS_INTEGER; -- character set form
cnt PLS_INTEGER; -- count of varray elements or number of
-- object attributes
sname VARCHAR2(35); -- schema name
type_name VARCHAR2(35); -- type name
version VARCHAR2(35);
BEGIN
FOR i IN 1 .. 5 LOOP
anydata_val := DBMS_DEFER_QUERY.GET_ANYDATA_ARG(call_no, i, txn_id);
-- Get the type information, including type name.
tc := anydata_val.GetType(t);
tc := t.GetInfo(prec, scale, len, csid, csfrm, sname, type_name,
version, cnt);
-- Based on the type name, convert the anydata value to the appropriate
-- user-defined types.
IF type_name = 'PHONE_LIST_TYP' THEN
-- The anydata_val contains phone_list_typ varray instance.
rval := anydata_val.GetCollection(data_pl);
-- Do something with data_pl.
ELSIF type_name = 'INVENTORY_LIST_TYP' THEN
-- anydata_val contains inventory_list_typ nested table instance.
rval := anydata_val.GetCollection(data_ntt);
-- Do something with data_ntt.
ELSIF type_name = 'WAREHOUSE_TYP' THEN
-- The anydata_val contains warehouse_typ object instance.
rval := anydata_val.GetObject(data_p);
-- Do something with data_p.
ELSIF type_name = 'INVENTORY_TYP' THEN
-- The anydata_val contains a reference to inventory_typ object instance.
rval := anydata_val.GetRef(ref1);
-- Do something with ref1.
END IF;
END LOOP;
END;
/
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Reference, Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Object-Relational Features, and Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about the ANYDATA datatype
As an administrator of a replication environment, you should regularly monitor the error queue to determine if any deferred transactions were not successfully applied at the target master site.
To check the error queue, issue the following SELECT statement (as the replication administrator) when connected to the target master site:
SELECT * FROM deferror;
If the error queue contains errors, then you should resolve the error condition and reexecute the deferred transaction. You have two options when reexecuting a deferred transaction: you can reexecute in the security context of the user who received the deferred transaction, or you can reexecute the deferred transaction with an alternate security context.
Caution:
If you have multiple error transactions and you want to make sure they are reexecuted in the correct order, then you can specifyNULL for the deferred_tran_id parameter in the procedures in the following sections. If you do not specify NULL, then reexecuting individual transactions in the wrong order can cause conflicts.The following procedure reexecutes a specified deferred transaction in the security context of the user who received the deferred transaction. This procedure should not be executed until the error situation has been resolved.
Meet the following requirements to complete these actions:
Executed As: Replication Administrator
Executed At: Site Containing Errors
Replication Status: Normal
Complete the following steps:
Step 1 Connect to the master site as the replication administrator.
CONNECT repadmin/repadmin@orc2.world
Step 2 Reexecute the error transaction.
BEGIN
DBMS_DEFER_SYS.EXECUTE_ERROR ( deferred_tran_id => '1.12.2904', destination => 'ORC2.WORLD'); END; /
The following procedure reexecutes a specified deferred transaction in the security context of the currently connected user. This procedure should not be executed until the error situation has been resolved.
Meet the following requirements to complete these actions:
Executed As: Connected User
Executed At: Site Containing Errors
Replication Status: Normal
Complete the following steps:
Step 1 Connect to the master site as the alternate user.
CONNECT hr/hr@orc2.world
Step 2 Reexecute the error transaction.
BEGIN
DBMS_DEFER_SYS.EXECUTE_ERROR_AS_USER ( deferred_tran_id => '1.12.2904', destination => 'ORC2.WORLD'); END; /