| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E25519-09 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E25519-09 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
A collection variable is a composite variable whose internal components, called elements, have the same data type. The value of a collection variable and the values of its elements can change.
You reference an entire collection by its name. You reference a collection element with the syntax collection(index).
PL/SQL has three kinds of collection types:
Associative array (formerly called PL/SQL table or index-by table)
Variable-size array (varray)
Nested table
An associative array can be indexed by either a string type or PLS_INTEGER. Varrays and nested tables are indexed by integers.
You can create a collection variable in either of these ways:
Define a collection type and then declare a variable of that type.
Use %TYPE to declare a collection variable of the same type as a previously declared collection variable.
Note:
This topic applies to collection types that you define inside a PL/SQL block or package, which differ from standalone collection types that you create with the "CREATE TYPE Statement".In a PL/SQL block or package, you can define all three collection types. With the CREATE TYPE statement, you can create nested table types and VARRAY types, but not associative array types.
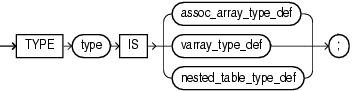
collection_type_definition ::=
See:
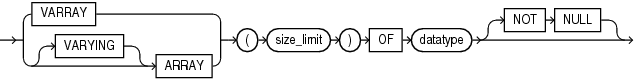
See "datatype ::=".
See:
Name of the collection type that you are defining.
Type definition for an associative array.
Restriction on assoc_array_type_def Can appear only in the declarative part of a block, subprogram, package specification, or package body.
Type definition for a nested table.
Type definition for a variable-size array.
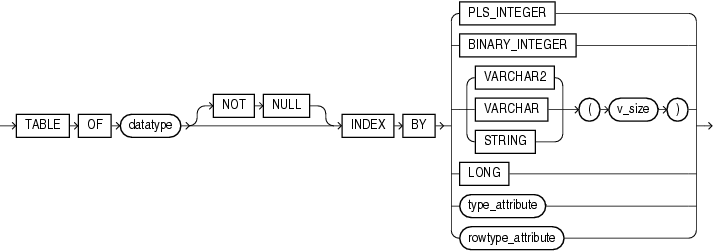
Data type of the elements of the associative array. datatype can be any PL/SQL data type except REF CURSOR.
Imposes the NOT NULL constraint on every element of the associative array. For information about this constraint, see "NOT NULL Constraint".
{ PLS_INTEGER | BINARY_INTEGER }
Specifies that the data type of the indexes of the associative array is PLS_INTEGER.
{ VARCHAR2 | VARCHAR | STRING } (v_size)
Specifies that the data type of the indexes of the associative array is VARCHAR2 (or its subtype VARCHAR or STRING) with length v_size.
You can populate an element of the associative array with a value of any type that can be converted to VARCHAR2 with the TO_CHAR function (described in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference).
Caution:
Associative arrays indexed by strings can be affected by National Language Support (NLS) parameters. For more information, see "NLS Parameter Values Affect Associative Arrays Indexed by String".Specifies that the data type of the indexes of the associative array is LONG, which is equivalent to VARCHAR2(32760).
Note:
Oracle supportsLONG only for backward compatibility with existing applications. For new applications, use VARCHAR2(32760).type_attribute, rowtype_attribute
Specifies that the data type of the indexes of the associative array is a data type specified with either %ROWTYPE or %TYPE. This data type must represent either PLS_INTEGER, BINARY_INTEGER, or VARCHAR2(v_size).
Maximum number of elements that the varray can have. size_limit must be an integer literal in the range from 1 through 2147483647.
Data type of the varray element. datatype can be any PL/SQL data type except REF CURSOR.
Imposes the NOT NULL constraint on every element of the varray. For information about this constraint, see "NOT NULL Constraint".
Data type of the elements of the nested table. datatype can be any PL/SQL data type except REF CURSOR or NCLOB.
If datatype is a scalar type, then the nested table has a single column of that type, called COLUMN_VALUE.
If datatype is an ADT, then the columns of the nested table match the name and attributes of the ADT.
Imposes the NOT NULL constraint on every element of the nested table. For information about this constraint, see "NOT NULL Constraint".
Name of a user-defined varray or nested table type (not the name of an associative array type).
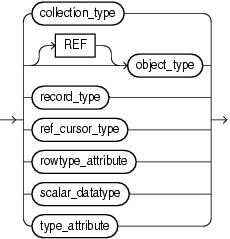
Instance of a user-defined type.
Name of a user-defined type that was defined with the data type specifier RECORD.
Name of a user-defined type that was defined with the data type specifier REF CURSOR.
Name of a scalar data type, including any qualifiers for size, precision, and character or byte semantics.
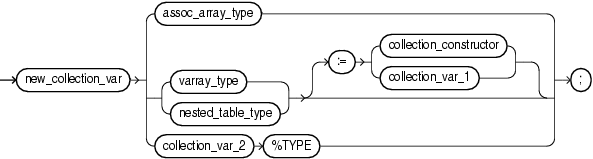
Name of the collection variable that you are declaring.
Name of a previously defined associative array type; the data type of new_collection_var.
Name of a previously defined VARRAY type; the data type of new_collection_var.
Name of a previously defined nested table type; the data type of new_collection_var.
Collection constructor for the data type of new_collection_var, which provides the initial value of new_collection_var.
Name of a previously declared collection variable of the same data type as new_collection_var, which provides the initial value of new_collection_var.
Note:
collection_var_1 and new_collection_var must have the same data type, not only elements of the same type.Name of a previously declared collection variable.
See "%TYPE Attribute".