| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
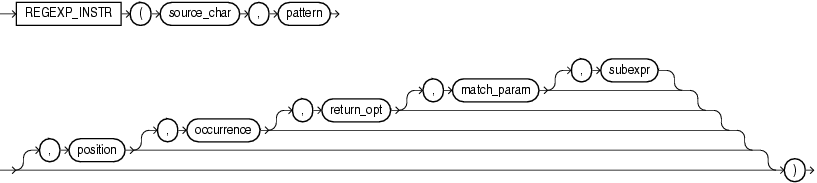
REGEXP_INSTR extends the functionality of the INSTR function by letting you search a string for a regular expression pattern. The function evaluates strings using characters as defined by the input character set. It returns an integer indicating the beginning or ending position of the matched substring, depending on the value of the return_option argument. If no match is found, then the function returns 0.
This function complies with the POSIX regular expression standard and the Unicode Regular Expression Guidelines. For more information, refer to Appendix D, "Oracle Regular Expression Support".
source_char is a character expression that serves as the search value. It is commonly a character column and can be of any of the data types CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB.
pattern is the regular expression. It is usually a text literal and can be of any of the data types CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, or NVARCHAR2. It can contain up to 512 bytes. If the data type of pattern is different from the data type of source_char, then Oracle Database converts pattern to the data type of source_char. For a listing of the operators you can specify in pattern, refer to Appendix D, "Oracle Regular Expression Support".
position is a positive integer indicating the character of source_char where Oracle should begin the search. The default is 1, meaning that Oracle begins the search at the first character of source_char.
occurrence is a positive integer indicating which occurrence of pattern in source_char Oracle should search for. The default is 1, meaning that Oracle searches for the first occurrence of pattern. If occurrence is greater than 1, then the database searches for the second occurrence beginning with the first character following the first occurrence of pattern, and so forth. This behavior is different from the INSTR function, which begins its search for the second occurrence at the second character of the first occurrence.
return_option lets you specify what Oracle should return in relation to the occurrence:
If you specify 0, then Oracle returns the position of the first character of the occurrence. This is the default.
If you specify 1, then Oracle returns the position of the character following the occurrence.
match_parameter is a text literal that lets you change the default matching behavior of the function. The behavior of this parameter is the same for this function as for REGEXP_COUNT. Refer to REGEXP_COUNT for detailed information.
For a pattern with subexpressions, subexpr is an integer from 0 to 9 indicating which subexpression in pattern is the target of the function. The subexpr is a fragment of pattern enclosed in parentheses. Subexpressions can be nested. Subexpressions are numbered in order in which their left parentheses appear in pattern. For example, consider the following expression:
0123(((abc)(de)f)ghi)45(678)
This expression has five subexpressions in the following order: "abcdefghi" followed by "abcdef", "abc", "de" and "678".
If subexpr is zero, then the position of the entire substring that matches the pattern is returned. If subexpr is greater than zero, then the position of the substring fragment that corresponds to subexpression number subexpr in the matched substring is returned. If pattern does not have at least subexpr subexpressions, the function returns zero. A null subexpr value returns NULL. The default value for subexpr is zero.
See Also:
The following example examines the string, looking for occurrences of one or more non-blank characters. Oracle begins searching at the first character in the string and returns the starting position (default) of the sixth occurrence of one or more non-blank characters.
SELECT
REGEXP_INSTR('500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA',
'[^ ]+', 1, 6) "REGEXP_INSTR"
FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR
------------
37
The following example examines the string, looking for occurrences of words beginning with s, r, or p, regardless of case, followed by any six alphabetic characters. Oracle begins searching at the third character in the string and returns the position in the string of the character following the second occurrence of a seven-letter word beginning with s, r, or p, regardless of case.
SELECT
REGEXP_INSTR('500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA',
'[s|r|p][[:alpha:]]{6}', 3, 2, 1, 'i') "REGEXP_INSTR"
FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR
------------
28
The following examples use the subexpr argument to search for a particular subexpression in pattern. The first statement returns the position in the source string of the first character in the first subexpression, which is '123':
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('1234567890', '(123)(4(56)(78))', 1, 1, 0, 'i', 1)
"REGEXP_INSTR" FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR
-------------------
1
The next statement returns the position in the source string of the first character in the second subexpression, which is '45678':
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('1234567890', '(123)(4(56)(78))', 1, 1, 0, 'i', 2)
"REGEXP_INSTR" FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR
-------------------
4
The next statement returns the position in the source string of the first character in the fourth subexpression, which is '78':
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('1234567890', '(123)(4(56)(78))', 1, 1, 0, 'i', 4)
"REGEXP_INSTR" FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR
-------------------
7