| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
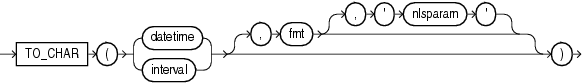
TO_CHAR (datetime) converts a datetime or interval value of DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND, or INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH data type to a value of VARCHAR2 data type in the format specified by the date format fmt. If you omit fmt, then date is converted to a VARCHAR2 value as follows:
DATE values are converted to values in the default date format.
TIMESTAMP and TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE values are converted to values in the default timestamp format.
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE values are converted to values in the default timestamp with time zone format.
Interval values are converted to the numeric representation of the interval literal.
Refer to "Format Models" for information on datetime formats.
The 'nlsparam' argument specifies the language in which month and day names and abbreviations are returned. This argument can have this form:
'NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = language'
If you omit 'nlsparam', then this function uses the default date language for your session.
The following example uses this table:
CREATE TABLE date_tab ( ts_col TIMESTAMP, tsltz_col TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, tstz_col TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE);
The example shows the results of applying TO_CHAR to different TIMESTAMP data types. The result for a TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE column is sensitive to session time zone, whereas the results for the TIMESTAMP and TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE columns are not sensitive to session time zone:
ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = '-8:00'; INSERT INTO date_tab VALUES ( TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-01 10:00:00'); INSERT INTO date_tab VALUES ( TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00', TIMESTAMP'1999-12-02 10:00:00 -8:00'); SELECT TO_CHAR(ts_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS ts_date, TO_CHAR(tstz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF TZH:TZM') AS tstz_date FROM date_tab ORDER BY ts_date, tstz_date; TS_DATE TSTZ_DATE ------------------------------ ------------------------------------- 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE, TO_CHAR(tsltz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS tsltz FROM date_tab ORDER BY sessiontimezone, tsltz; SESSIONTIM TSLTZ ---------- ------------------------------ -08:00 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE = '-5:00'; SELECT TO_CHAR(ts_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS ts_col, TO_CHAR(tstz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF TZH:TZM') AS tstz_col FROM date_tab ORDER BY ts_col, tstz_col; TS_COL TSTZ_COL ------------------------------ ------------------------------------- 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 01-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 02-DEC-1999 10:00:00.000000 -08:00 SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE, TO_CHAR(tsltz_col, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SSxFF') AS tsltz_col FROM date_tab ORDER BY sessiontimezone, tsltz_col; 2 3 4 SESSIONTIM TSLTZ_COL ---------- ------------------------------ -05:00 01-DEC-1999 13:00:00.000000 -05:00 02-DEC-1999 13:00:00.000000
The following example converts an interval literal into a text literal:
SELECT TO_CHAR(INTERVAL '123-2' YEAR(3) TO MONTH) FROM DUAL; TO_CHAR ------- +123-02