| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) E41084-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
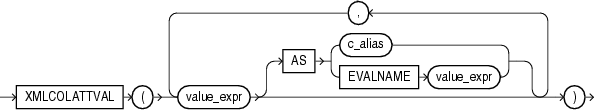
XMLColAttVal creates an XML fragment and then expands the resulting XML so that each XML fragment has the name column with the attribute name.
You can use the AS clause to change the value of the name attribute to something other than the column name. You can do this by specifying c_alias, which is a string literal, or by specifying EVALNAME value_expr. In the latter case, the value expression is evaluated and the result, which must be a string literal, is used as the alias. The alias can be up to 4000 characters.
You must specify a value for value_expr. If value_expr is null, then no element is returned.
Restriction on XMLColAttVal You cannot specify an object type column for value_expr.
The following example creates an Emp element for a subset of employees, with nested employee_id, last_name, and salary elements as the contents of Emp. Each nested element is named column and has a name attribute with the column name as the attribute value:
SELECT XMLELEMENT("Emp",
XMLCOLATTVAL(e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.salary)) "Emp Element"
FROM employees e
WHERE employee_id = 204;
Emp Element
--------------------------------------------------------------------
<Emp>
<column name="EMPLOYEE_ID">204</column>
<column name="LAST_NAME">Baer</column>
<column name="SALARY">10000</column>
</Emp>
Refer to the example for XMLFOREST to compare the output of these two functions.