| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B28051-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B28051-03 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes how to run the Automatic Database Diagnostics Monitor (ADDM) manually to monitor current and historical database performance. Typically, you should use the automatic diagnostic feature of ADDM to identify performance problems with the database. As described in Chapter 3, "Automatic Database Performance Monitoring", ADDM runs once every hour by default, and it is possible to configure ADDM to run more or less frequently. However, there may be some cases where you may want to run ADDM manually.
For example, you may notice significant performance degradation that did not exist in the previous ADDM analysis period, and the next ADDM analysis is not scheduled to run for another 30 minutes. In this case, you may want to run ADDM manually before the next scheduled ADDM analysis to immediately identify and resolve the performance problem.
Another case of when you may want to run ADDM manually is if you want to analyze a longer time period than one ADDM analysis period. For example, you may want to analyze the database performance in a full workday by analyzing 8 consecutive hours of database activity. One way to do this is to analyze each of the individual ADDM analysis within this 8-hour period. However, this may become complicated if there are performance problems that exist for only part of the 8-hour period, because they may appear in only some of the individual ADDM analysis. Alternatively, you can run ADDM manually using a pair of AWR snapshots that encompass the 8-hour period, and ADDM will identify the most critical performance problems in the entire time period.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Manually Running ADDM to Analyze Current Database Performance
Manually Running ADDM to Analyze Historical Database Performance
Although ADDM runs every hour by default to analyze snapshots taken by the AWR during that period, it is possible to run ADDM manually to analyze current database performance. This can be very useful if you notice a drop in current performance level, or a sudden spike in database activity on the Database Performance page, as described in Chapter 4, "Monitoring Real-Time Database Performance".
When you run ADDM manually, a manual AWR snapshot is created automatically. This may impact the ADDM run cycle. For example, if you scheduled ADDM to run hourly at the start of each hour and the last ADDM run was at 8:00 p.m., running ADDM manually at 8:30 p.m. will cause the next scheduled ADDM run to start at 9:30 p.m., not 9:00 p.m. All subsequent ADDM run will continue on the new run cycle, occurring hourly at the half-hour instead of the start of each hour.
To analyze current database performance by manually running ADDM:
On the Database Home page, under Related Links, click Advisor Central.
The Advisor Central page appears.
Under Advisors, click ADDM.
The Run ADDM page appears.
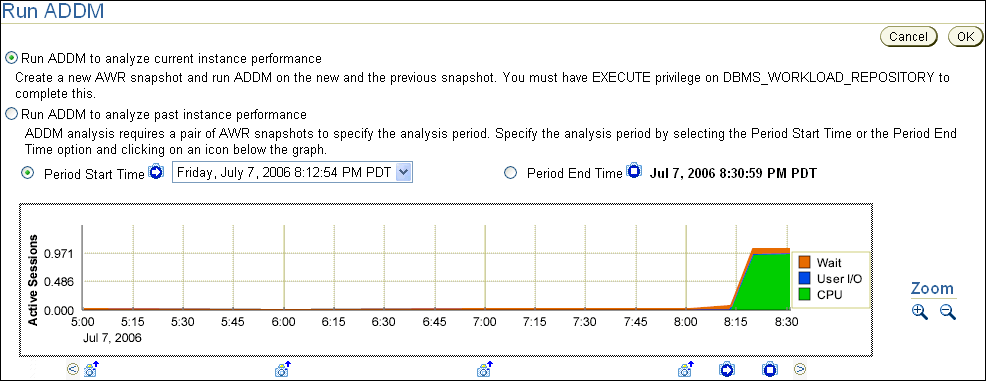
In this example, CPU usage spiked in the last 10 minutes.
Select Run ADDM to analyze current instance performance and click OK.
The Confirmation page appears.
On the Confirmation page, click Yes.
The Processing: Run ADDM Now page appears while a new AWR snapshot is taken, and an ADDM run is performed on the time period between the new and the previous snapshot.
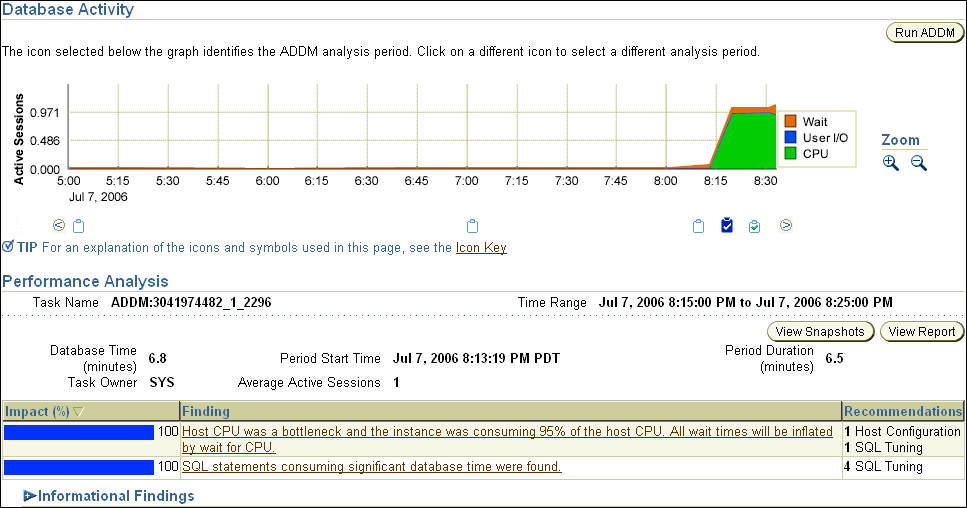
After ADDM completes the analysis, the Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor (ADDM) page appears with the results of the ADDM run, as shown on Figure 6-1.
The results of the ADDM task can also be viewed in a report that can be saved for later access. To view the ADDM report, click View Report.
For information about reviewing ADDM results, see "Reviewing the Automatic Database Diagnostics Monitor Analysis".
Figure 6-1 Analyzing Current Database Performance
You can run ADDM manually to analyze historical database performance by selecting a pair or range of AWR snapshots as the analysis period. This is useful when you have identified a specific time period in the past when the database performance was poor.
You can monitor historical database performance using the Database Performance page by selecting Historical from the View Data list. In Historical view, you can monitor database performance in the past, up to the duration defined by the AWR retention period. If you notice any performance degradation, you can drill down to appropriate pages from the Database Performance page to identify historical performance problems with the database, as described in Chapter 4, "Monitoring Real-Time Database Performance". If a historical performance problem is identified, you can choose to run ADDM manually to analyze that particular time period.
To analyze historical database performance by manually running ADDM:
On the Database Home page, under Related Links, click Advisor Central.
The Advisor Central page appears.
Under Advisors, click ADDM.
The Run ADDM page appears.
Select Run ADDM to analyze past instance performance.
Specify a time period for analysis by selecting a pair of AWR snapshots.
To select snapshots:
Select Period Start Time.
Below the graph for the starting snapshot, click the snapshot you want to use for the start time.
A play icon (displayed as an arrow) appears over the snapshot icon. In this example, database activity peaked from 10:15 p.m. to 11:00 p.m., so the snapshot taken at 10:15 p.m. is selected for the start time.
Select Period End Time.
Below the graph for the ending snapshot, click the snapshot you want to use for the end time.
A stop icon (displayed as a square) appears over the snapshot icon. In this example, the snapshot taken at 11:00 p.m. is selected.
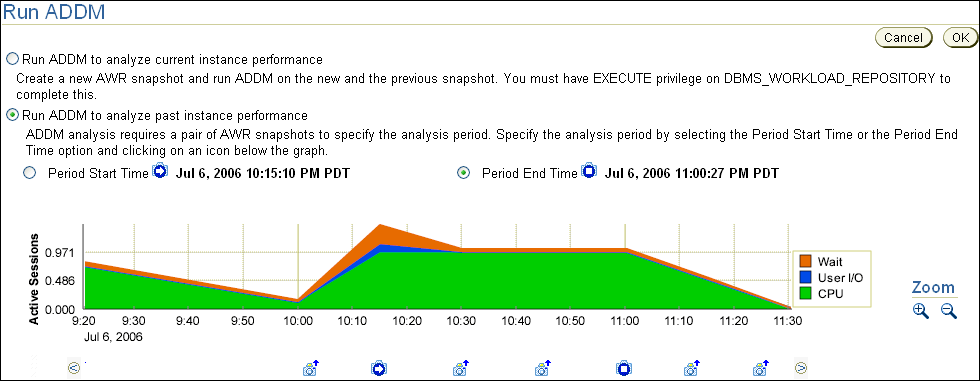
Click OK.
After ADDM completes the analysis, the Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor (ADDM) page appears with the results of the ADDM run, as shown on Figure 6-2.
The results of the ADDM task can also be viewed in a report that can be saved for later access. To view the ADDM report, click View Report.
For information about reviewing ADDM results, see "Reviewing the Automatic Database Diagnostics Monitor Analysis".
Figure 6-2 Analyzing Historical Database Performance
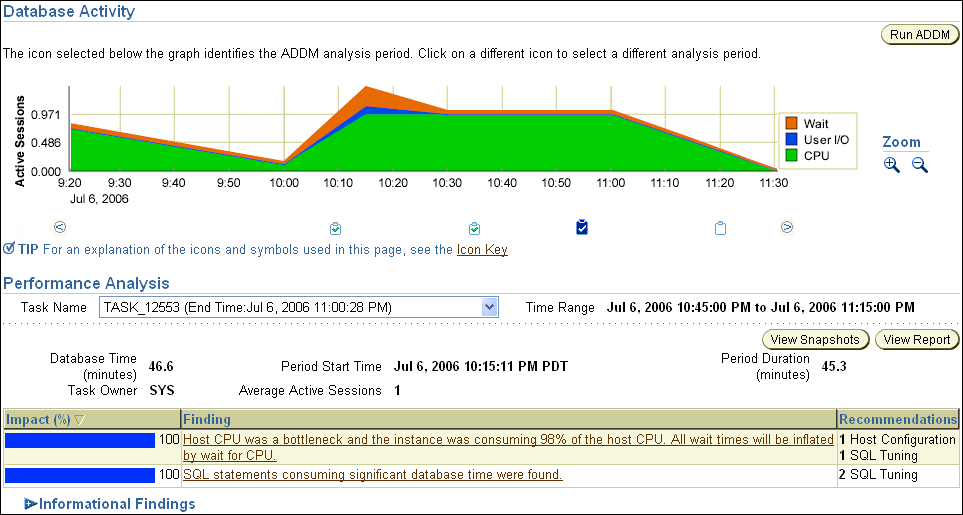
If you ran ADDM manually to analyze current or historical database performance, the results are displayed on the Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor (ADDM) page after the ADDM run has completed.
You can access the ADDM results at a later time, or access the ADDM results from previous executions.
On the Database Home page, under Related Links, click Advisor Central.
The Advisor Central page appears.
Under Advisor Tasks, select ADDM for Advisory Type and the appropriate search criteria and click Go.
For example, you may want to select All for Advisor Runs to view all ADDM tasks.
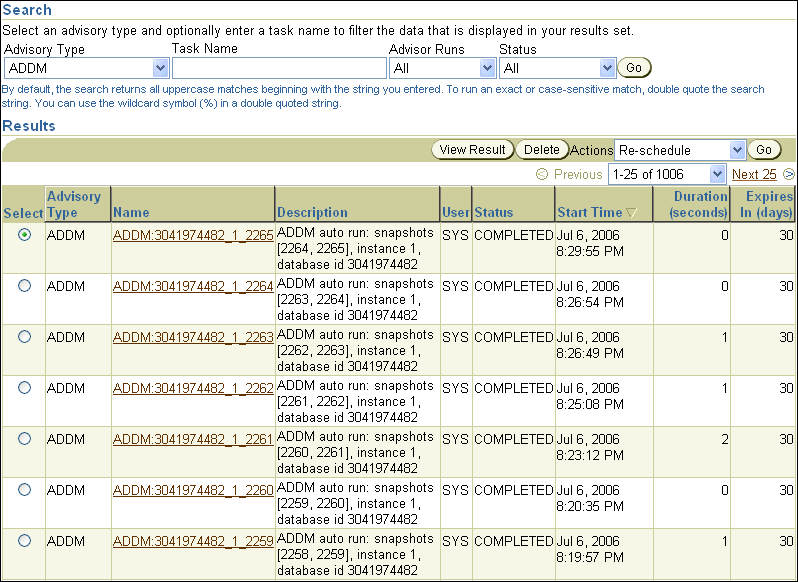
The ADDM tasks are displayed under Results. To view an ADDM result, select the desired ADDM task and click View Result.
The results from the selected ADDM task are displayed in the Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor (ADDM) page.